Fungal Collection (page 9)
"Fungal Kingdom: Exploring the Intricate World of Fungi" Budding yeast cell: Witness the remarkable process of reproduction as a budding yeast cell emerges
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
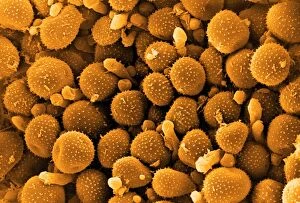
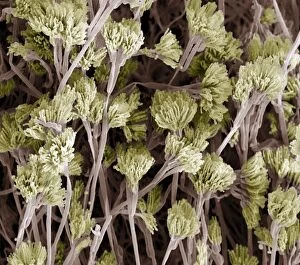
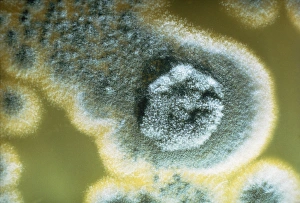
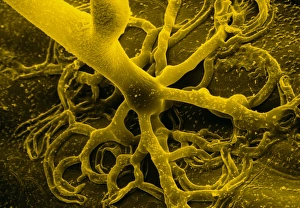
"Fungal Kingdom: Exploring the Intricate World of Fungi" Budding yeast cell: Witness the remarkable process of reproduction as a budding yeast cell emerges, ready to create new life. Fly agaric mushrooms: Delve into the enchanting realm of fly agaric mushrooms, with their vibrant red caps and white spots, captivating both nature enthusiasts and fairytale lovers alike. SEM of penicillin fungus: Uncover the microscopic beauty of penicillin fungus through scanning electron microscopy (SEM), revealing its intricate structures that have revolutionized medicine. Culture of Aspergillus nidulans fungus: Step into a laboratory where cultures of Aspergillus nidulans fungus thrive, showcasing their unique growth patterns and potential for scientific research. Cep mushroom (Boletus edulis): Discover the culinary delight known as cep mushroom or Boletus edulis, renowned for its rich flavor and sought-after by chefs around the world. Candida fungus, SEM: Explore the unseen world within our bodies as Candida fungi are magnified under an electron microscope, shedding light on their role in various infections and diseases. Mushroom gills, SEM: Marvel at the intricate network of gills found beneath mushroom caps when observed through scanning electron microscopy (SEM), highlighting their crucial role in spore production. Fly agaric fungi: Journey through enchanted forests where fly agaric fungi flourish; these iconic red-and-white toadstools evoke a sense of wonderment while harboring fascinating ecological relationships with other organisms. Dividing yeast cells, SEM: Peer into a microscopic universe where dividing yeast cells undergo mitosis under high-resolution imaging techniques—witnessing life's continuous cycle unfold before your eyes. Penicillium roqueforti fungus: Meet Penicillium roqueforti—a blue mold used in cheese-making—whose distinctive flavor and appearance contribute to the creation of beloved blue cheeses worldwide.