Scanning Electron Microscope Collection (page 8)
"Unveiling the Hidden World
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
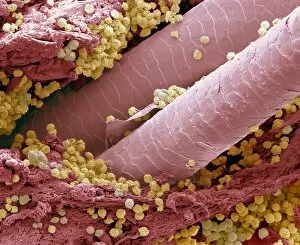
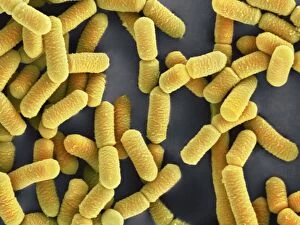
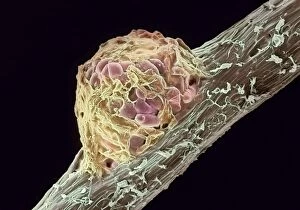
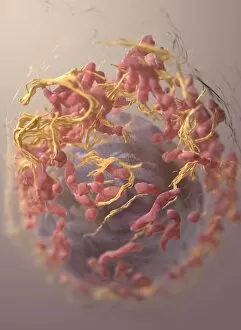
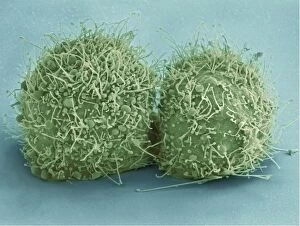
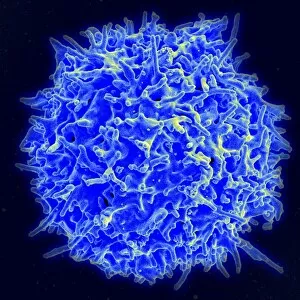
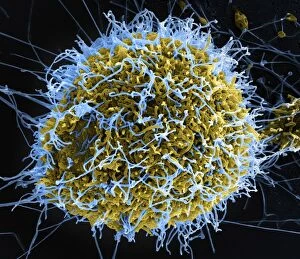
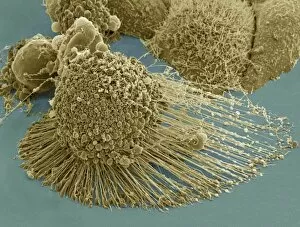
"Unveiling the Hidden World: Exploring with a Scanning Electron Microscope" The scanning electron microscope (SEM) is an incredible tool that allows us to delve into the microscopic realm, revealing intricate details and unlocking secrets of the unseen. With its high magnification capabilities, it offers a glimpse into fascinating aspects of life and nature. In one captivating image, we witness the beauty of gender determination as X and Y chromosomes are captured under the SEM's lens. The intricate patterns and structures within these chromosomes showcase the complexity of our genetic makeup. Moving on to another astonishing discovery, a Scanning Electron Micrograph presents us with an up-close view of a Praying Mantis at 30 times magnification. Every tiny detail becomes visible, from its delicate limbs to its mesmerizing eyes – reminding us of nature's remarkable diversity. Shifting focus to plant life, lavender pollen grains come alive in another SEM image. These minuscule particles take center stage as their unique shapes and textures become apparent under intense scrutiny. Zooming in even further reveals a Tardigrade or 'Water Bear' at an astounding 1250 times magnification. This resilient creature captures our imagination as we explore its alien-like features through this powerful imaging technique. Delving deeper into biological wonders, T lymphocytes battling cancer cells are showcased in yet another breathtaking SEM capture. This visual representation highlights the ongoing fight within our bodies against diseases like cancer – emphasizing both hope and resilience. Calcareous phytoplankton takes center stage next as we uncover their intricate forms through SEM imagery. These microscopic organisms play crucial roles in marine ecosystems while leaving us awe-inspired by their stunningly detailed structures. Transitioning to neural marvels, nerve cells reveal their intricacy under the watchful eye of an SEM. Their branching extensions create complex networks that enable communication throughout our bodies – showcasing nature's ingenuity at work. Venturing into insect realms once again, a fruit fly is immortalized under the SEM's lens.