Microscopic Photos Collection (page 2)
Discovering the hidden wonders of the microscopic world is like entering a realm of infinite fascination
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
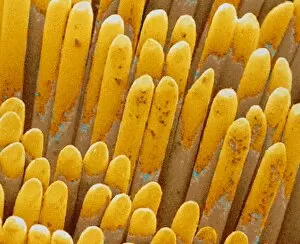
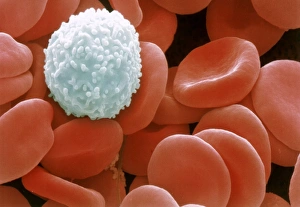
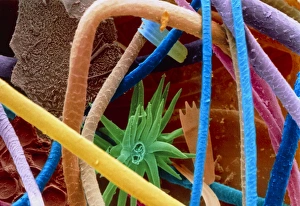
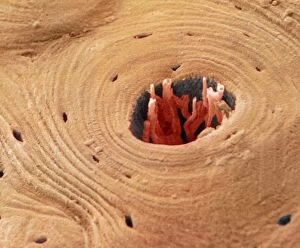
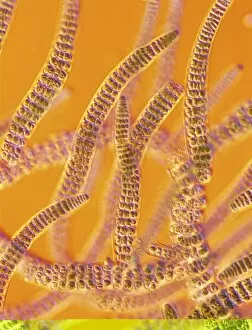
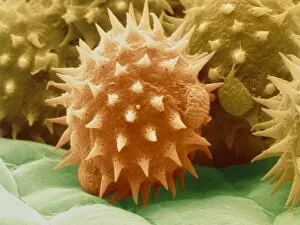
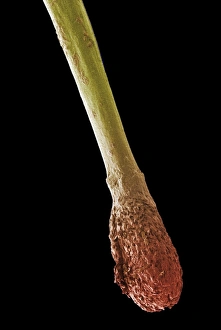
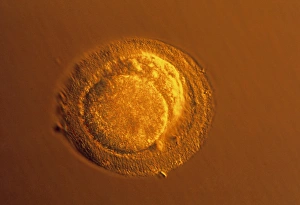
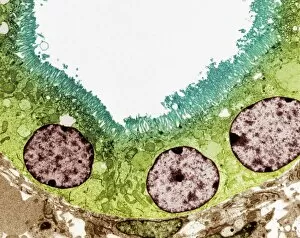
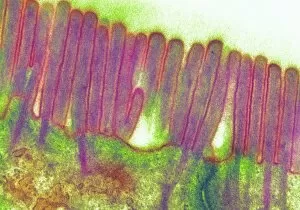
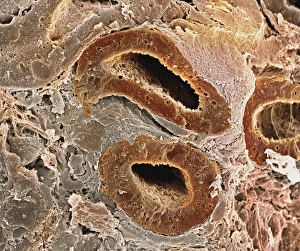
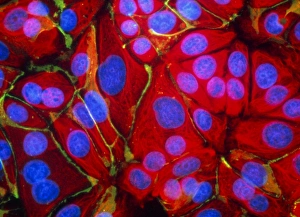
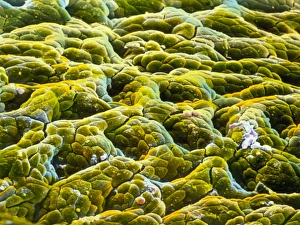
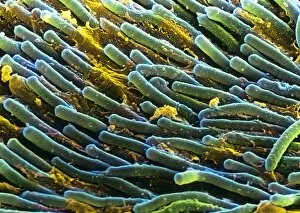
Discovering the hidden wonders of the microscopic world is like entering a realm of infinite fascination. From particle tracks leaving trails of mystery to the mesmerizing bubble chamber photo capturing the decay of a sigma particle, these microscopic photos unveil secrets that lie beyond our naked eye's reach. One remarkable image showcases the first observation of an omega-minus particle, a groundbreaking moment in scientific history. Meanwhile, another snapshot reveals the delicate beauty of a human blastocyst, reminding us of life's miraculous beginnings. Immunofluorescent LM offers us glimpses into intricate networks within our own bodies - neurons and astrocytes intricately woven together like cosmic constellations. And then there are oxytocin hormone crystals, their vibrant colors shining through as if encapsulating love itself. The iris of an eye captured by SEM reminds us that even something as ordinary as our eyes holds extraordinary complexity when seen up close. Similarly, osteoporotic bone under SEM unveils its fragile structure with astonishing detail. Light micrographs bring forth stunning images such as oxytocin crystals glistening like precious gems or spiral spore chains formed by Streptomyces bacteria resembling ethereal works of art. And let us not forget about our retina - a gateway to vision and perception - or nerve cells firing messages at lightning speed throughout our bodies, orchestrating every movement and thought we have. These microscopic photos offer more than just visual delight; they invite us to ponder upon the vastness contained within each minuscule frame. They remind us that sometimes it is in exploring the smallest details that we gain profound insights into ourselves and the world around us.