Fluorescent Collection (page 6)
"Unveiling the Vibrant World of Fluorescent Cell Imaging: From Cerebellum Tissue to Dividing Cells" Illuminating the intricate beauty within our brains
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
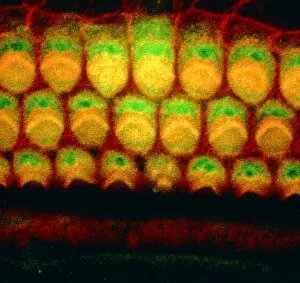
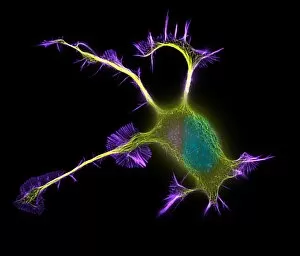
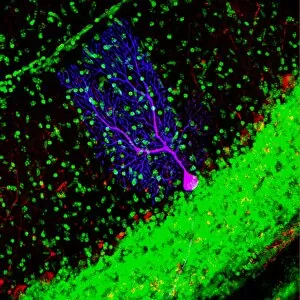
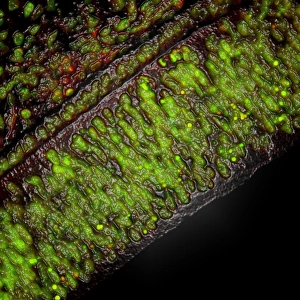
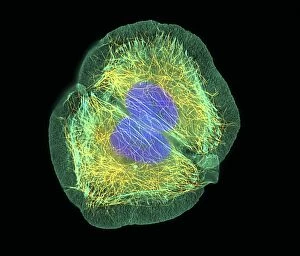
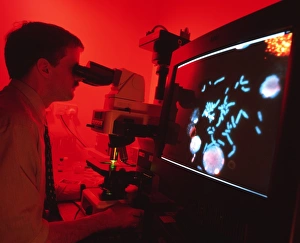
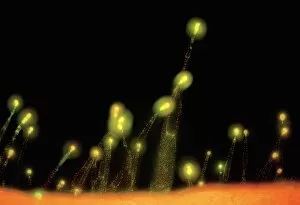
"Unveiling the Vibrant World of Fluorescent Cell Imaging: From Cerebellum Tissue to Dividing Cells" Illuminating the intricate beauty within our brains, a light micrograph reveals the mesmerizing patterns of cerebellum tissue. Dive into the microscopic realm as glial cells come alive under a confocal light micrograph, showcasing their fluorescent brilliance. HeLa cells take center stage in this captivating light micrograph (C017 / 8299), displaying their striking fluorescence and cellular structure. Witness another stunning view of HeLa cells (C017 / 8298) through a microscope lens, where their vibrant hues reveal hidden secrets within. Journey into the cerebral cortex and marvel at its nerve cells' fluorescent glow, illuminating the complexity of our brain's architecture. Witness the miracle of life itself as cell division unfolds before your eyes in this breathtaking fluorescent micrograph. Returning to explore cerebellum tissue once more, a light micrograph captures its ethereal essence with radiant colors dancing across each frame. The Metropolitan Police launch on the River Thames may seem unrelated but shares an unexpected connection - fluorescence can be found everywhere. Behold nature's perpetual cycle as dividing cells showcase their vivid fluorescence in yet another awe-inspiring image captured by microscopy techniques. Intriguing and visually stunning, these fluorescent hints offer glimpses into various aspects of cellular biology and beyond – from delicate tissues to bustling cityscapes – reminding us that even at microscopic levels, there is beauty all around us waiting to be discovered.