Auditory Collection
"Exploring the Wonders of Auditory Perception
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
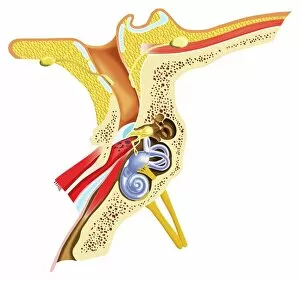
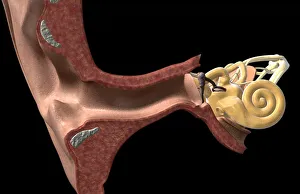
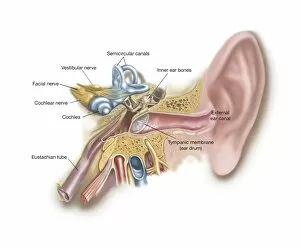
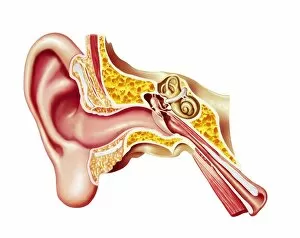
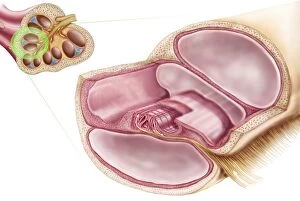
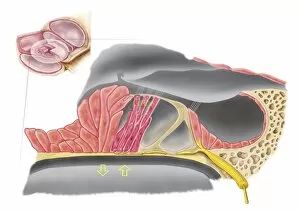
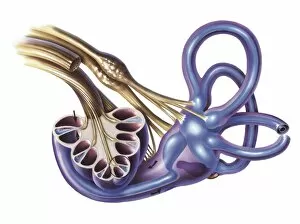
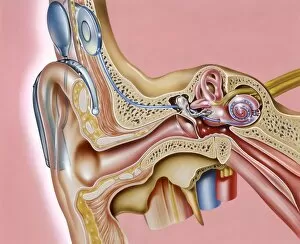
"Exploring the Wonders of Auditory Perception: From Anatomy to Music" Discovering the intricate world perception is like unraveling a captivating symphony within our very own bodies. Through scientific illustrations, we can delve into the fascinating anatomy that enables us to experience sound in all its glory. Intriguing diagrams showcase the inner ear's complexity, with its auditory canal leading to the eardrum and connecting to vital components such as semicircular canals, cochlea, cochlear nerve, and even the eustachian tube. These illustrations provide a visual gateway into understanding how our ears capture and process sound waves. Transporting ourselves from anatomical depictions to historical landmarks, we encounter Paris' magnificent Auditory of the Church of Invalides. A black-and-white photograph captures this architectural marvel where echoes of prayers once reverberated through its walls – an auditory testament to faith and devotion. Venturing further into history's embrace, an allegorical artwork portrays human hearing intertwined with music itself. This enchanting portrayal reminds us that music holds a profound connection with our ability to perceive sounds; it transcends language barriers and speaks directly to our souls. Shifting gears towards practicality, an engraving reveals how one Free Church in Scotland employed innovative ventilation techniques within their auditoriums. By ensuring fresh air circulation during gatherings or sermons, they prioritized both comfort and optimal acoustic experiences for their congregations. Returning back to anatomy's realm, detailed images shed light on facial nerves intricately connected with our auditory system – emphasizing how these two senses intertwine harmoniously within us. Additionally, we explore cross-sections unveiling the wonders housed within the cochlear duct while also examining labels guiding us through external auditory canals. The journey concludes by embracing comprehensive views encompassing inner ear structures alongside sinuses – reminding us of nature's remarkable design where multiple systems coexist seamlessly within our bodies.