Voltaic Pile Collection
The voltaic pile, also known as the Voltaic battery, is a remarkable invention that revolutionized the world of electricity
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
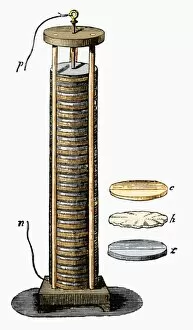
The voltaic pile, also known as the Voltaic battery, is a remarkable invention that revolutionized the world of electricity. Developed by Italian physicist Alessandro Volta in 1800, this device paved the way for modern batteries and power sources. One captivating image from history showcases The Royal Institution electric battery, depicted in Les Merveilles de la Science publication from 1870. This illustration captures the intricate design of the voltaic pile and highlights its significance in scientific exploration. Another vibrant lithograph portrays Voltas battery, showcasing its colorful components and intricate structure. It serves as a visual testament to the ingenuity behind this groundbreaking invention. Intriguingly, an enchanting costume called "The Electricity Fairy" was created for a fancy dress ball around 1885. This imaginative attire incorporated a miniature battery into its design, emphasizing how deeply embedded it had become in popular culture. A chromolitho artwork depicts Alessandro Volta himself explaining his revolutionary battery's principle to none other than Napoleon Bonaparte in 1800. This encounter between two great minds symbolizes how significant this invention was even at that time. An additional chromolitho portrait of Alessandro Volta showcases his dedication to science and innovation. His contributions to physics through inventions like the voltaic pile solidified his place among history's greatest scientists. The wet pile version of Voltas' battery is captured beautifully in an image from 1800. Its simplicity yet effectiveness demonstrates why it became widely adopted across various fields requiring portable power sources during that era. Count Alessandro Volta (1745-1827), an Italian physicist whose brilliance knew no bounds when it came to electrical discoveries, is immortalized through another striking chromolitho portrait by an unknown artist. His legacy lives on through his groundbreaking work with batteries and electricity generation systems. These captivating images provide glimpses into both historical moments and artistic interpretations surrounding one man's invention that changed the course of science.