Osteocyte Collection
Osteocytes: The Guardians of Our Bones In the intricate world of bone tissue, osteocytes play a vital role in maintaining our skeletal health
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
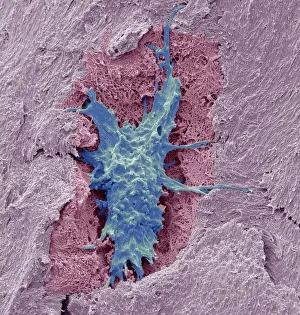
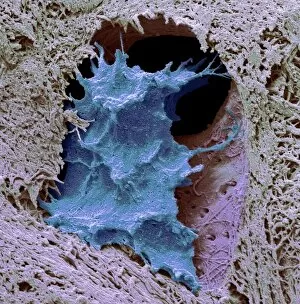
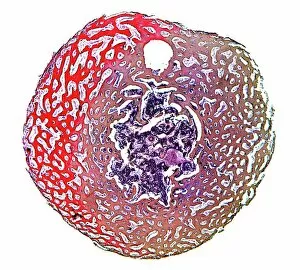
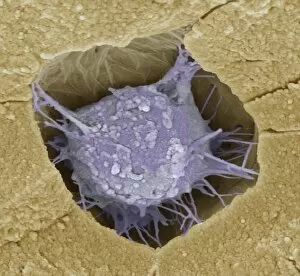
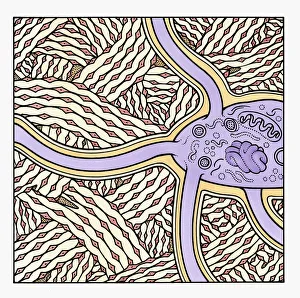
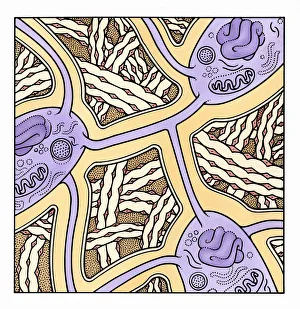
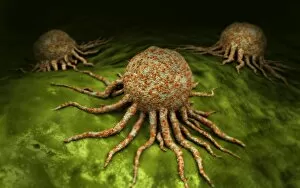
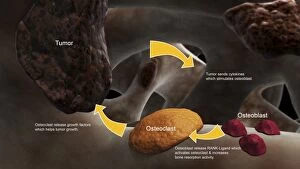
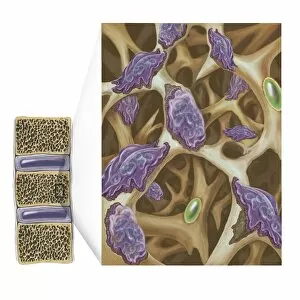
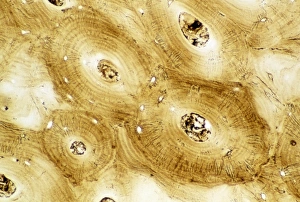
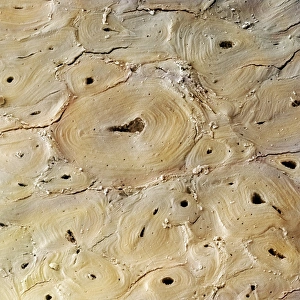
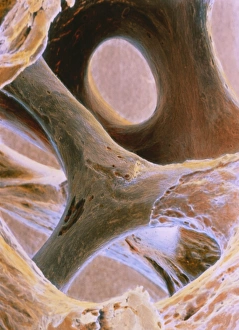
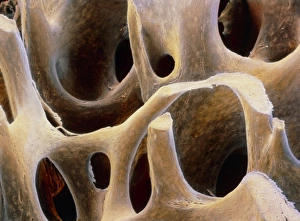
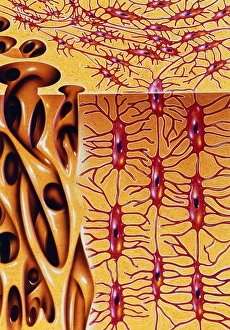
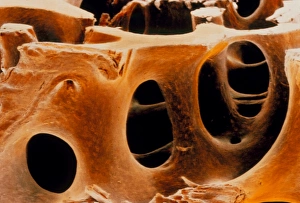
Osteocytes: The Guardians of Our Bones In the intricate world of bone tissue, osteocytes play a vital role in maintaining our skeletal health. These remarkable cells are found within both compact and spongy bone, as revealed by light micrographs capturing their delicate structures. Under the scanning electron microscope (SEM), osteocytes appear even more fascinating. With SEM C016/9025 and SEM C016/9026 images, we can observe their complex network of slender extensions that connect them to neighboring cells and blood vessels. This intricate web allows osteocytes to communicate with each other and receive essential nutrients for proper functioning. Illustrations depicting the formation of human bones showcase how osteocytes contribute to this process. They actively participate in bone remodeling, constantly renewing our skeleton throughout life. However, when faced with conditions like osteoporosis, these illustrations reveal the detrimental effects on bone density caused by decreased activity or an imbalance between bone formation and resorption. Speaking of resorption, another captivating image shows osteoclasts at work - specialized cells responsible for breaking down old or damaged bone tissue. Their crucial role becomes evident in preventing fractures and ensuring healthy bones. But not all invaders are beneficial; conceptual images depict cancer viruses infiltrating our bodies. Although unrelated to normal osteocyte function, these visuals serve as a reminder that diseases can disrupt the balance within our bones too.