Neuroscience Collection (page 3)
"Unraveling the Mysteries of the Mind: Exploring Neuroscience through Art and Science" Delve into the intricate world of neuroscience
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
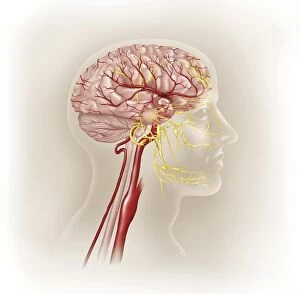
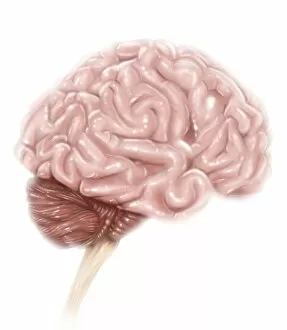
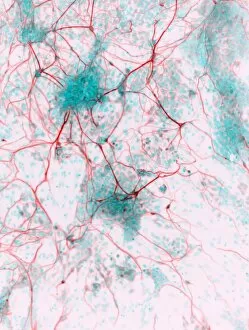
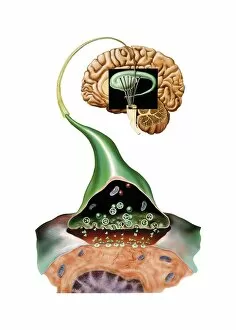
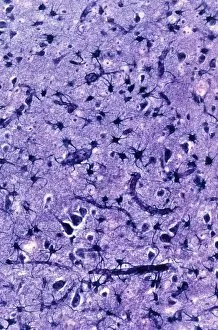
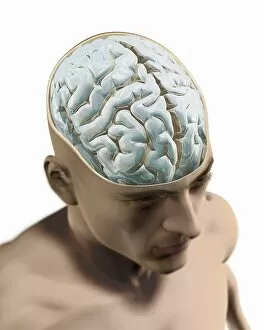
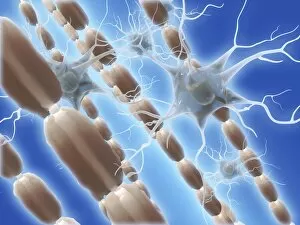
"Unraveling the Mysteries of the Mind: Exploring Neuroscience through Art and Science" Delve into the intricate world of neuroscience, where art meets science to unravel the complexities of the human brain. Starting with an inferior view, witness a captivating portrayal of its anatomy, showcasing the mesmerizing Medulla Oblongata – a vital structure responsible for controlling essential bodily functions. Moving to a superior view, be enchanted by colored lobes and labels that demystify different regions within our brain. Marvel at how these distinct areas work in harmony to shape our thoughts, emotions, and actions. Prepare to question your perception as you encounter mind-bending artwork like the Hollow-face illusion. Witness how our brains can be deceived by optical tricks, highlighting their remarkable ability to interpret reality. Venturing further into lateral views of human brain anatomy reveals another fascinating aspect – glial cells. Observe them through confocal light micrography; these unsung heroes play crucial roles in supporting neurons and maintaining overall brain health. Returning once more to artistic interpretations, explore additional illusions such as Ouchi illusion and Goblet illusion. These captivating artworks challenge our understanding of visual perception while reminding us that our brains are constantly processing information in unique ways. But it's not all about illusions; we must also acknowledge the importance of blood supply within brain tissue. Discover how this intricate network ensures oxygenation and nourishment for optimal cognitive function. Concluding this journey is yet another stunning artwork depicting various aspects of brain anatomy. Reflect on what you have learned throughout this exploration - from structural intricacies to perceptual wonders - gaining a deeper appreciation for neuroscience's ongoing quest to understand one of humanity's greatest enigmas.