Membrane Collection (page 6)
The intricate anatomy of the human ear is beautifully depicted in this lithograph, published in 1876
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
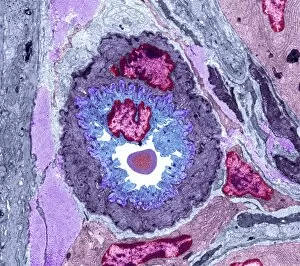
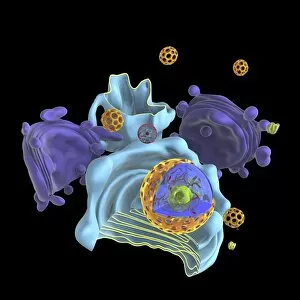
The intricate anatomy of the human ear is beautifully depicted in this lithograph, published in 1876. One notable feature highlighted here is the membrane, which plays a crucial role in transmitting sound waves to our auditory system. Moving on to cellular structures, the rough endoplasmic reticulum (ER) takes center stage under a transmission electron microscope (TEM). This network of membranes within cells is responsible for protein synthesis and transport. Artwork showcasing different cell types also emphasizes the significance of membranes. From the delicate cell membrane itself, represented by artwork C013 / 7467, to mitochondria seen through TEM imaging - these organelles possess their own unique membranes that regulate various cellular functions. Intriguingly, even chloroplasts have their own distinct membrane structure as revealed by artwork dedicated to studying photosynthesis. These specialized organelles found in plants are responsible for converting sunlight into energy. Beyond biology, membranes find relevance elsewhere too. Think about damp-proofing measures taken in houses – membranes act as barriers against moisture infiltration and protect our living spaces from potential damage. However, not all mentions of they are positive. Bacterial meningitis can be detected through MRI scans where inflammation affects the protective brain meninges' integrity. Understanding how pathogens breach these defensive layers helps diagnose and treat such infections effectively. Nature's wonders also exhibit fascinating adaptations involving membranes; take Plecotus sp. , commonly known as long-eared bats with their remarkable hearing abilities thanks to specialized ear membrane structures aiding echolocation skills. Zooming into finer details under TEM again reveals eye muscles' intricate arrangement (TEM C014 / 1468), highlighting how well-organized muscle fibers rely on precise membranous connections for coordinated movement and vision control. Lastly, let's not forget intestinal microvilli observed through TEM – finger-like projections covered by plasma membrane lining our intestines play a vital role in nutrient absorption during digestion processes. From ancient lithographs to modern imaging techniques, the significance of membranes spans across various fields.