Histological Collection (page 2)
"Exploring the Intricacies of Histological Wonders: Unveiling the Hidden Beauty within Our Bodies" Step into the fascinating world of histology
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
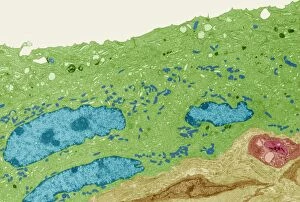
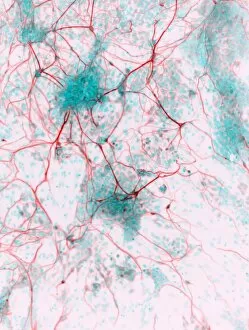
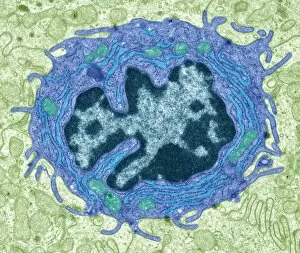
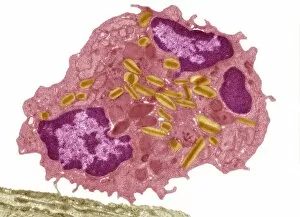
"Exploring the Intricacies of Histological Wonders: Unveiling the Hidden Beauty within Our Bodies" Step into the fascinating world of histology, where microscopic wonders come to life. Delve into Santiago Ramon Y Cajal's masterpiece, as his cortical grey matter schema unveils the intricate network that forms our brain's command center. Witness the mesmerizing complexity of a mammalian retina through a histological diagram, revealing how light is transformed into vision. Journey deeper into our cerebellum tissue, as a captivating light micrograph showcases its unique structure and function. Marvel at Ramon Y Cajal's genius once again as he unravels the secrets of synapse nerve junctions through an astonishing TEM image. Venture further into uncharted territory with a glimpse of hippocampus brain tissue, where memories are formed and stored. Observe Purkinje nerve cells in the cerebellum, their elegant arrangement hinting at their crucial role in coordinating movement. Witness nature's precision with kidney tubules in section; these delicate structures filter waste from our bloodstreams tirelessly. Explore human brain microscope slides and be awestruck by its intricate architecture - billions of neurons working harmoniously to shape who we are. Peer closely at rough endoplasmic reticulum through TEM imagery; this cellular powerhouse orchestrates protein synthesis within each living cell. Immerse yourself in glial stem cell culture under a light microscope - witness new life being nurtured for potential regeneration. Finally, marvel at the intricacy of brain tissue blood supply - countless vessels ensuring oxygen and nutrients reach every corner of this remarkable organ. Histological wonders unlock hidden beauty within us all – reminding us that even on a microscopic level, there is awe-inspiring complexity waiting to be discovered.