False Colour Collection
"Unveiling the Hidden Beauty: Exploring False Colour in Microscopy and Imaging" Step into a world where reality meets artistry
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
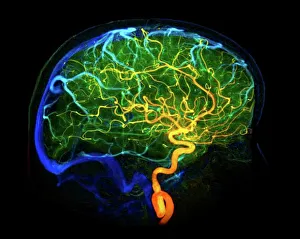
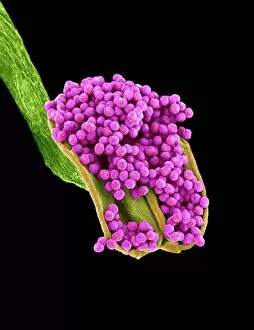
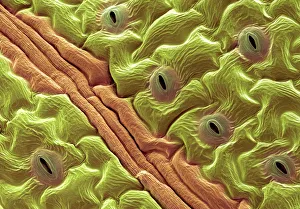
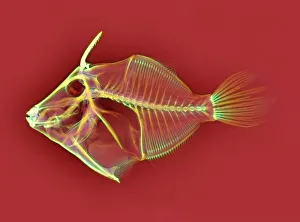
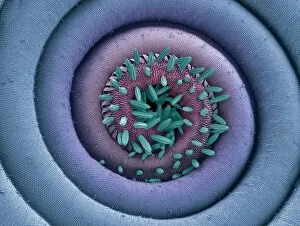
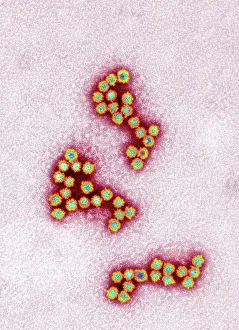
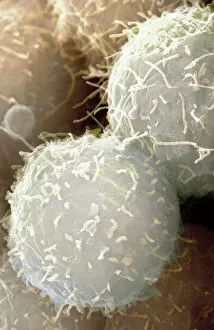
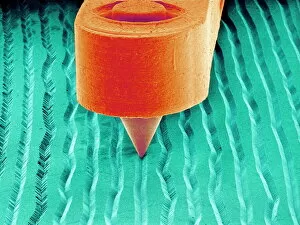
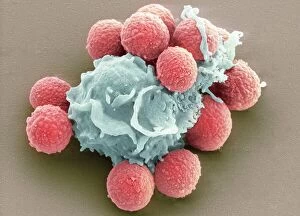
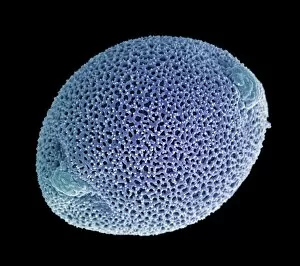
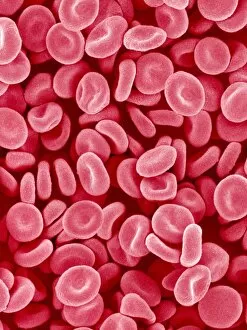
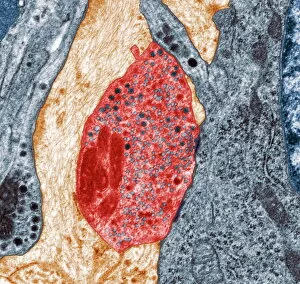
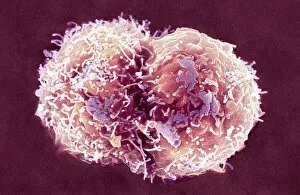
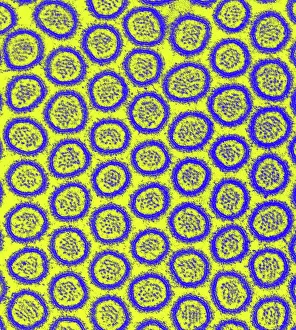
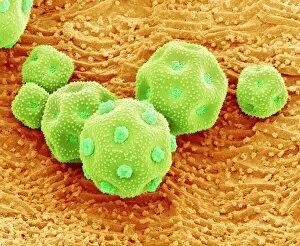
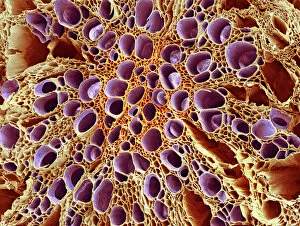
"Unveiling the Hidden Beauty: Exploring False Colour in Microscopy and Imaging" Step into a world where reality meets artistry, as we delve into the captivating realm of "false colour. " In this mesmerizing journey, we encounter an array of intricate subjects that have been transformed through advanced imaging techniques. Brace yourself for a visual feast that transcends our conventional perception. First up, behold the brain's intricate network of blood vessels captured in a 3D angiogram from 1981. Through false colour enhancement, these delicate pathways come alive with vibrant hues, revealing their hidden complexity. Moving on to nature's wonders, prepare to be enchanted by the Geranium anther under scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Its microscopic details are unveiled in vivid shades, showcasing its remarkable structure and beauty. Next on our exploration is Dahlia flower pollen also observed under SEM. The once minuscule grains now emerge as magnificent orbs adorned with striking colours—a testament to nature's exquisite design. Venturing further into the microscopic realm, we encounter diatoms—tiny algae—with their intricately patterned shells. Under SEM and enhanced with false colouring techniques, these diatoms transform into kaleidoscopic masterpieces that blur the line between science and art. But it doesn't stop there. Witness an ant like never before through SEM; its exoskeleton becomes a work of art when illuminated by vibrant tones. Meanwhile, X-ray imaging reveals the intricate skeleton of a triggerfish—an ethereal display reminiscent of otherworldly creatures lurking beneath ocean depths. Delving deeper within cells brings us face-to-face with rough endoplasmic reticulum—the cellular factory responsible for protein synthesis. Enhanced by false colouring using transmission electron microscopy (TEM), this complex network takes on an otherworldly appearance akin to futuristic cityscapes bathed in neon lights. Shifting gears towards medical marvels captured via X-ray technology unveils both the functional and aesthetic aspects of our bodies.