Eumycota Collection (page 4)
Eumycota, the diverse kingdom of fungi, encompasses a fascinating array of organisms
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
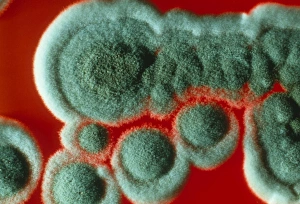
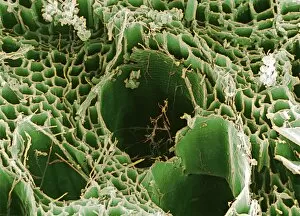
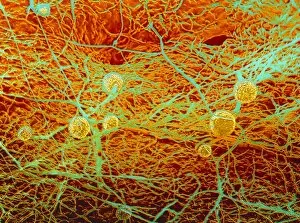
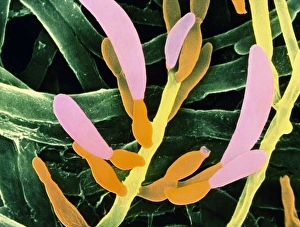
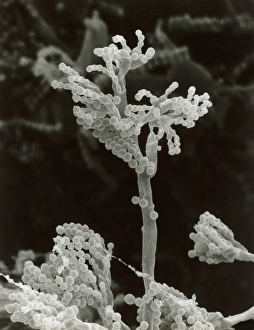
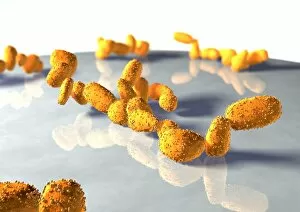
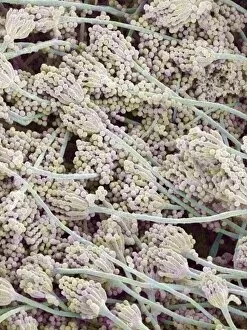
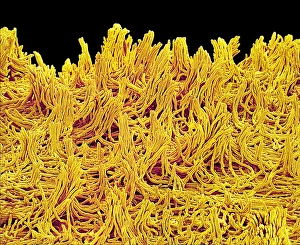
Eumycota, the diverse kingdom of fungi, encompasses a fascinating array of organisms. From the microscopic world of budding yeast cells and dividing yeast cells seen through scanning electron microscopy (SEM), to the enchanting fly agaric mushrooms with their distinctive red caps and white spots, this caption explores some captivating members of Eumycota. In our first glimpse into this kingdom, we encounter the SEM image of penicillin fungus - a remarkable organism that has revolutionized medicine by producing antibiotics. Moving on to Aspergillus nidulans fungus in culture, its intricate structures captivate us as it thrives in laboratory conditions. Nature's artistry is showcased through the Cep mushroom or Boletus edulis - an edible delicacy prized for its rich flavor and meaty texture. The SEM image of mushroom gills reveals their intricate network responsible for spore production and dispersal. Fly agaric fungi transport us into fairy tales with their vibrant colors and whimsical appearance. These iconic mushrooms have long been associated with folklore and mythical creatures. Returning to the microscopic realm, we witness dividing yeast cells under SEM once again - a testament to their incredible ability to reproduce rapidly. Penicillium roqueforti fungus takes center stage next; known for its role in aging blue cheeses like Roquefort, it adds distinct flavors as it grows within these culinary delights. Fruiting bodies of Rhizopus oligosporus catch our attention next – these structures are essential for reproduction in this species while Cryptococcus neoformans fungi reveal themselves under light microscopy (LM). This pathogenic fungus can cause severe infections particularly in individuals with compromised immune systems. Eumycota truly showcases nature's diversity at both macroscopic and microscopic levels. Whether they provide sustenance or pose health risks, these organisms remind us how intricately interconnected our world is with fungi playing vital roles across various ecosystems.