Botanical Science Collection
"Exploring the Intricate World of Botanical Science: Unveiling the Secrets Within Plant Cells" Delving into the fascinating realm of botanical science
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
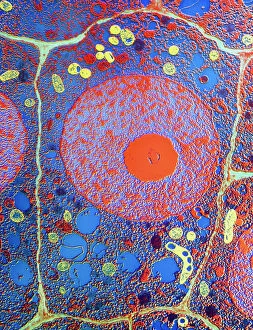
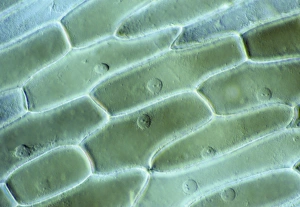
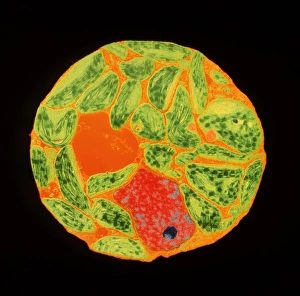
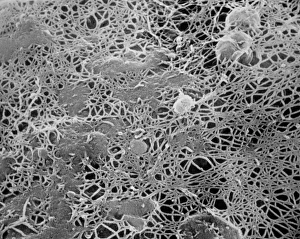
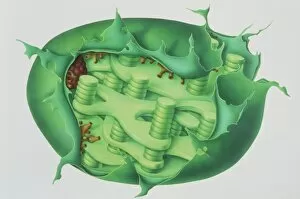
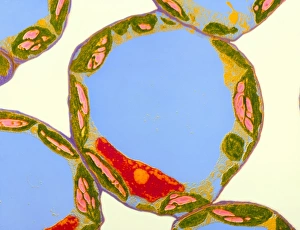
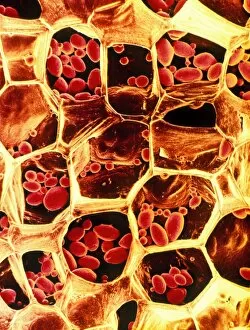
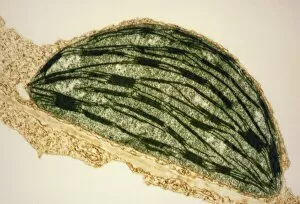
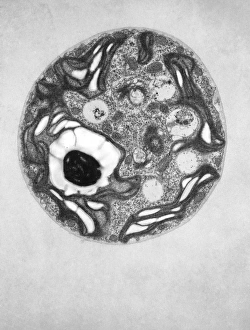
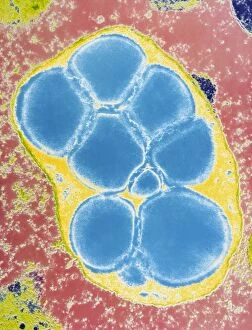
"Exploring the Intricate World of Botanical Science: Unveiling the Secrets Within Plant Cells" Delving into the fascinating realm of botanical science, we uncover a world teeming with microscopic wonders. Peering through our microscope lens, we are captivated by the mesmerizing sight of chloroplasts in the cells of a pea plant. These tiny green powerhouses harness sunlight to convert it into energy, fueling life itself. Moving deeper into the intricate web of plant cell structures, we witness mitosis in action – a breathtaking dance where cells divide and multiply. Underneath our light micrograph's gaze, this process reveals its awe-inspiring beauty and complexity. Shifting focus to another staple crop, potato cells unveil their hidden treasure - starch grains. Like precious jewels scattered within these humble tubers, these grains serve as vital energy reserves for both plants and humans alike. Venturing further into nature's laboratory, an onion's epidermis beckons us with its captivating cellular landscape. Through our trusty light microscope lens once again, we marvel at each individual cell forming this protective layer on an onion bulb's surface. Starch grains dotting these cells provide sustenance while adding yet another layer of intrigue to their existence. As our exploration continues, we stumble upon a remarkable connection between nuclear envelopes and endoplasmic reticulum (ER). This interplay highlights nature's ingenuity in orchestrating complex systems within even the tiniest components of life. Finally, peering deep inside tobacco protoplasts reveals chloroplasts – miniature factories producing food through photosynthesis. These vibrant green organelles remind us that plants hold not only beauty but also incredible resilience and adaptability. In every corner lies a universe waiting to be discovered; from chloroplasts capturing sunlight to starch grains storing energy or even nuclei connecting with ER networks – each revelation brings us closer to unraveling nature’s secrets.