Thrombus Collection
"Thrombus: The Silent Intruder Within Our Bloodstream" Blood clotting is a vital process that helps our bodies heal wounds and prevent excessive bleeding
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
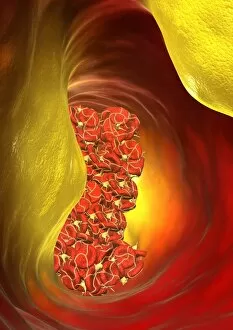
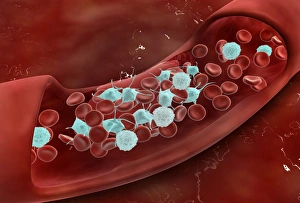
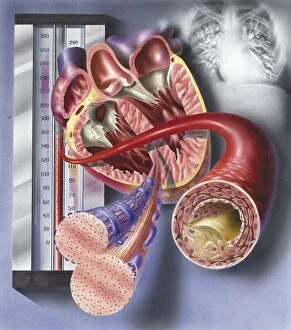
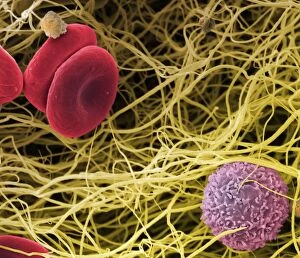
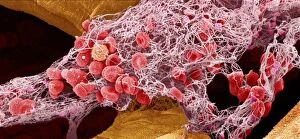
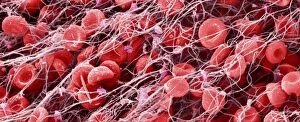
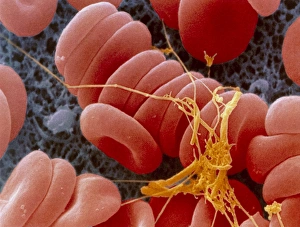
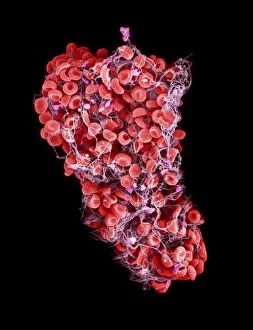
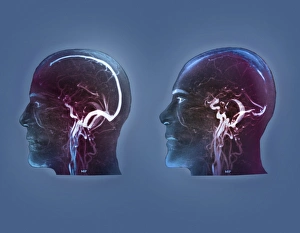
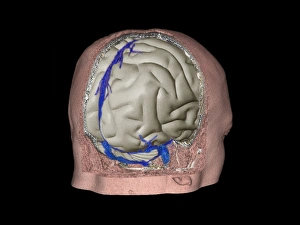
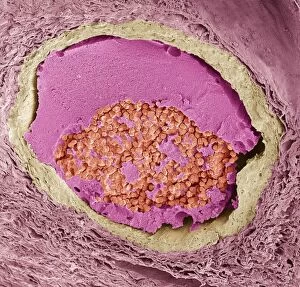
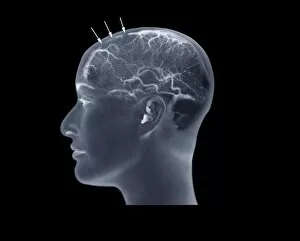
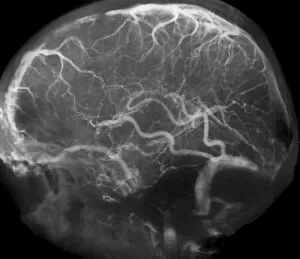
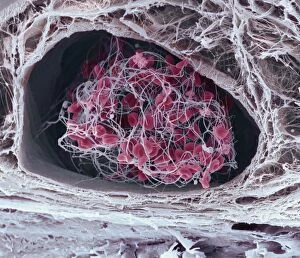
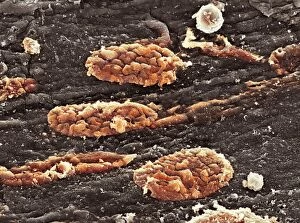
"Thrombus: The Silent Intruder Within Our Bloodstream" Blood clotting is a vital process that helps our bodies heal wounds and prevent excessive bleeding. However, when this mechanism goes awry, they can lead to the formation of a thrombus, commonly known as a blood clot. SEM C016 / 9747 captures the intricate web-like structure of these clots, showcasing their complexity. Deep vein thrombus (DVT) is one such example where blood clots form within deep veins, often in the legs. SEM imagery provides us with an up-close look at these potentially dangerous formations. Artwork C016 / 4619 depicts another perspective on blood clotting, highlighting how thrombosed blood vessels can impede normal circulation. Similarly, blocked arteries are illustrated through computer artwork, emphasizing the potential consequences of arterial obstruction. Biomedical illustrations offer insight into various stages of skin damage and repair involving thrombi. Cross-section images reveal how fibroblasts multiply and migrate to injured areas while forming plugs within the thrombus itself (C013 / 4649). As time progresses, these plugs contract and shrink as new skin tissue forms underneath. The impact of thrombi extends beyond just surface-level injuries; they also play a significant role in cardiovascular health. Arteries on heart visuals expose the presence of atherosclerotic plaque within an artery - contributing to conditions like coronary artery disease. Microscopic views further emphasize the dangers posed by blood clotting inside arteries - increasing risks for strokes or heart attacks if left untreated. Additionally, acute coronary syndrome highlights microvascular obstructions caused by these clots' presence. Understanding and managing thrombi is crucial for maintaining overall well-being. By unraveling their complexities through advanced imaging techniques and biomedical illustrations alike, we gain valuable insights into preventing life-threatening complications associated with abnormal blood clot formation.