Staphylococcus Aureus Collection
Staphylococcus aureus, commonly known as MRSA (Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
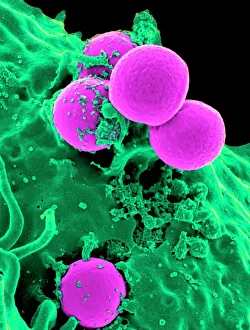
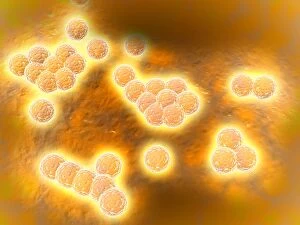
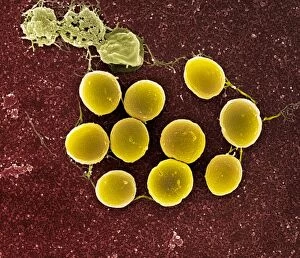
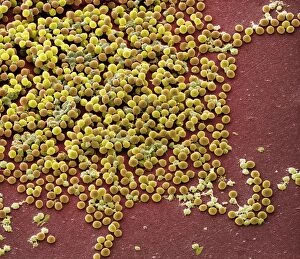
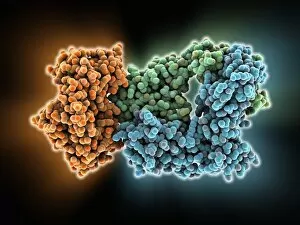
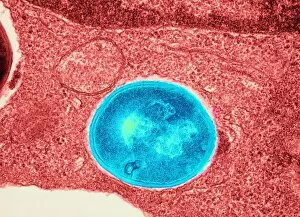
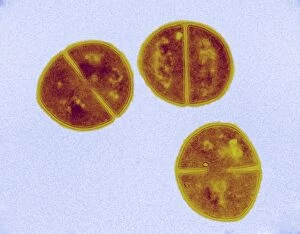
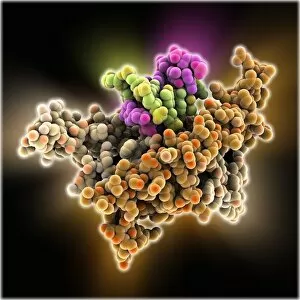
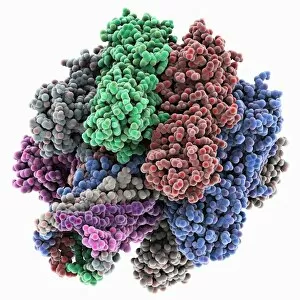
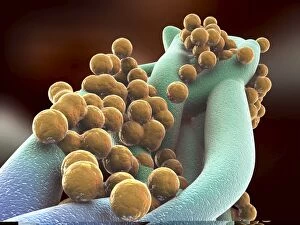
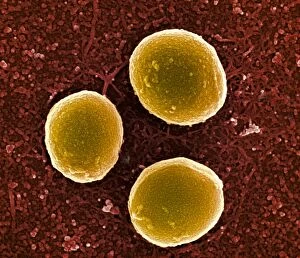
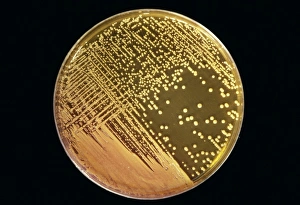
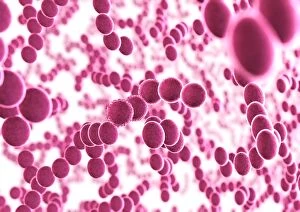
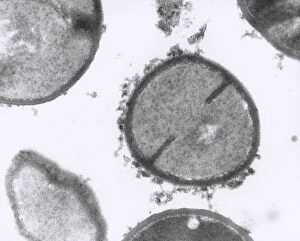
Staphylococcus aureus, commonly known as MRSA (Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus), is a highly resistant strain of bacteria that poses a significant threat to human health. In this captivating image, we witness the battle between our immune system and this formidable pathogen. The first glimpse reveals a neutrophil engulfing MRSA, showcasing the body's defense mechanism in action. This microscopic view showcases the tenacity bacteria, which can cause various skin diseases as depicted in an ancient lithography from 1895. Further magnification allows us to explore the intricate details of these resilient microbes. The SEM C018 / 8596 captures their distinct shape and arrangement, while another microscopic view emphasizes their presence within our bodies. However, it is the alarming sight of Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus that truly grabs attention. These strains have developed resistance against multiple antibiotics, making them incredibly difficult to treat effectively. The repeated images emphasize their prevalence and significance in medical research. In one striking colorized scanning electron micrograph, we witness a white blood cell devouring MRSA—a testament to our immune system's relentless fight against infection. Another scanning electron micrograph highlights how human neutrophils actively ingest MRSA particles for elimination. These visuals serve as reminders of both the beauty and danger presented by staphylococcus bacteria. Understanding their behavior and developing effective treatments are crucial steps towards combating this persistent threat to public health.