Platelets Collection
Platelets play a crucial role in the intricate process of blood coagulation cascade
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
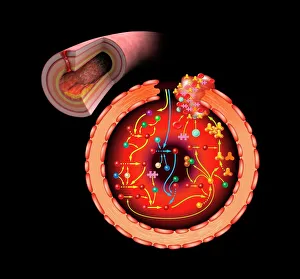
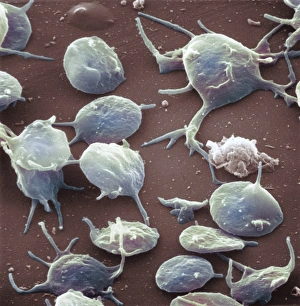
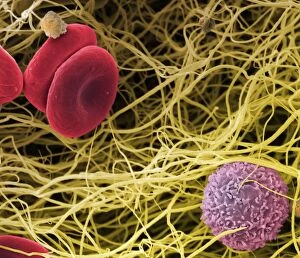
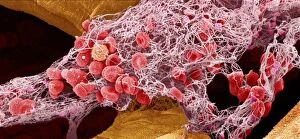
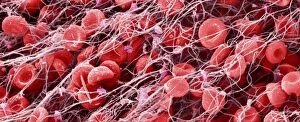
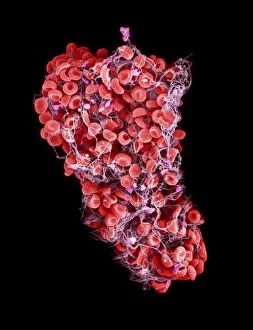
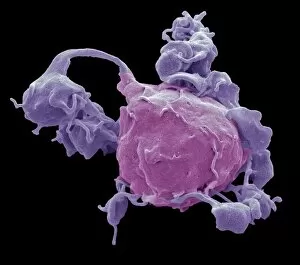
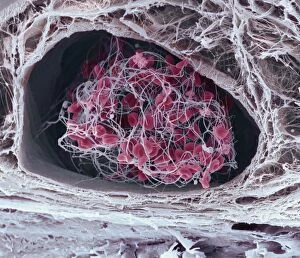
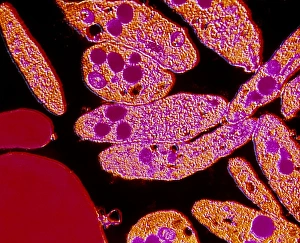
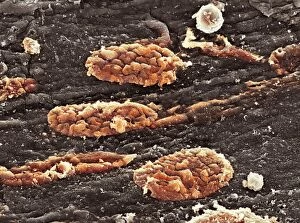
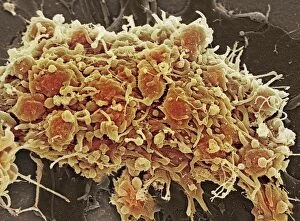
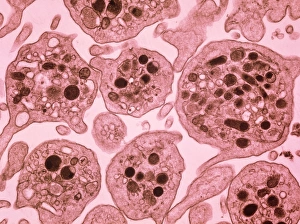
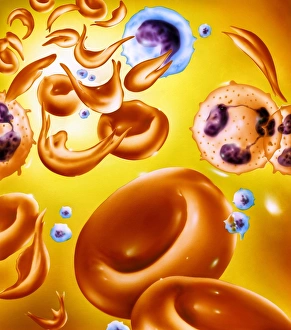
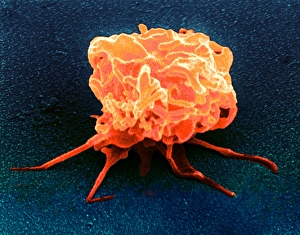
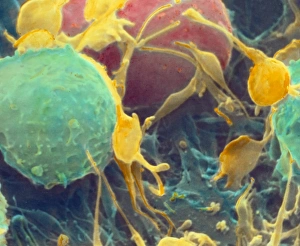
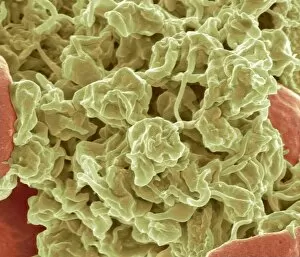
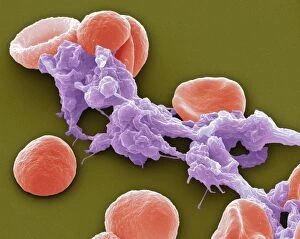
Platelets play a crucial role in the intricate process of blood coagulation cascade. These tiny, disc-shaped cells are like the unsung heroes of our circulatory system, working tirelessly to prevent excessive bleeding and promote healing. In the mesmerizing artwork C016 / 9873, platelets take center stage as they gather around a blood clot, their mission clear: to seal off any wounds and restore balance within our bodies. This microscopic view captured by SEM reveals their intricate structure and highlights their importance in maintaining our health. When an injury occurs, platelets rush to the scene, forming a plug that stops bleeding. In SEM images such as C016 / 9747 or C017 / 7141, we witness these remarkable cells interweaving with fibrin strands to create a robust blood clot, and is through this collaboration between platelets and other components of our blood that we can avoid potentially life-threatening hemorrhages. SEM images like C016 / 9750 or C016 / 9752 showcase platelets alongside white blood cells – another essential component of our immune system. Together, they form an army against infections and work synergistically to maintain homeostasis within us. As we marvel at these captivating visuals provided by science, let us not forget the vital role played by platelets in safeguarding our well-being. They may be small individually but collectively possess immense power when it comes to ensuring proper wound healing and preventing excessive bleeding. So next time you see a drop of your own precious red fluid escaping from your body's protective barrier, remember those incredible little warriors called platelets who come rushing in for your rescue.