Particle Physics Laboratory Collection
Step into the fascinating world of particle physics at the Particle Physics Laboratory, where groundbreaking discoveries and cutting-edge experiments take place
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
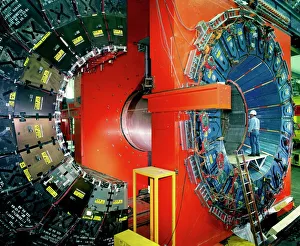
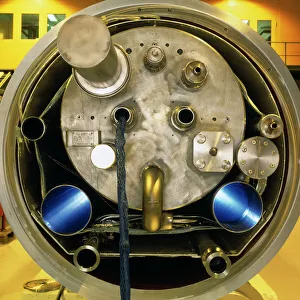
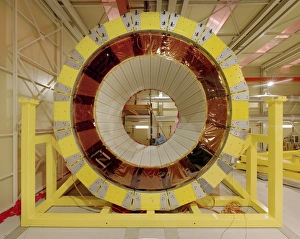
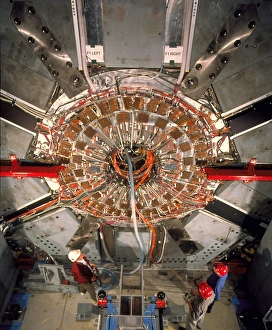
Step into the fascinating world of particle physics at the Particle Physics Laboratory, where groundbreaking discoveries and cutting-edge experiments take place. In this captivating mock-up of the Large Hadron Collider at CERN, scientists delve deep into the mysteries of the universe. The CDF particle detector at Fermilab captures elusive particles, unraveling their secrets one by one. Meanwhile, the HERA accelerator ring at DESY propels particles to unimaginable speeds, unlocking new realms of knowledge. Venturing further underground, we find ourselves in the LEP collider tunnel at CERN. Here, scientists push boundaries and explore uncharted territories with unparalleled precision. Testing magnets for the Large Hadron Collider ensures that every component is finely tuned for optimal performance. The H1 particle detector stands as a testament to human ingenuity and scientific prowess. It meticulously records data from high-energy collisions, providing invaluable insights into subatomic phenomena. At Fermilab's Tevatron particle collider, particles collide head-on in a mesmerizing display of energy exchange. As we approach completion of the magnet for the Large Hadron Collider, anticipation fills the air. This monumental feat will pave the way for unprecedented discoveries about our universe's fundamental building blocks. Inside LEP particle collider at CERN lies a realm where matter and antimatter meet in an intricate dance – offering glimpses into cosmic puzzles yet unsolved. The Advanced Light Source synchrotron illuminates previously unseen realms with its powerful beams of light. Within L3 particle detector at CERN resides a team of dedicated technicians tirelessly working to ensure accurate measurements and precise results - their expertise crucial to unraveling nature's deepest secrets. Witnessing a technician engrossed in his work within OPAL detector brings forth an appreciation for meticulous craftsmanship behind these complex machines - each part contributing towards expanding our understanding of existence itself. At Particle Physics Laboratory, curiosity knows no bounds as humanity strives to unlock nature’s most profound enigmas.