Nuclei Collection
"Nuclei: The Intricate Powerhouses within Our Cells and Beyond" Delving into the microscopic world, we encounter the mesmerizing beauty of nuclei
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
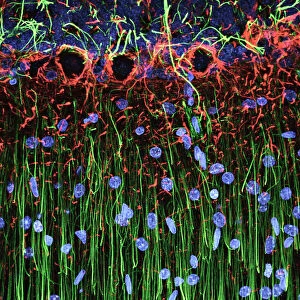
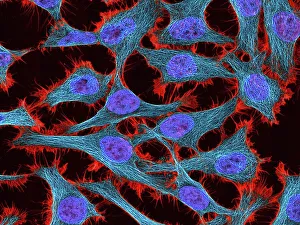
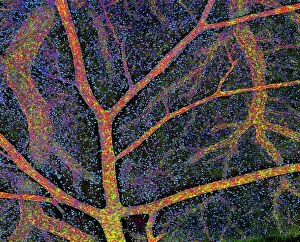
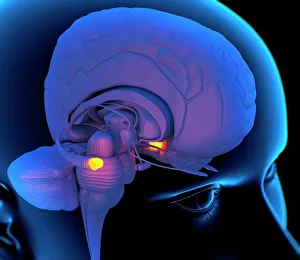
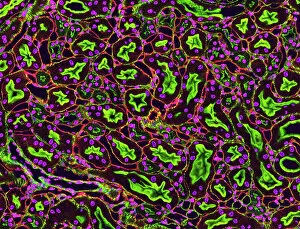
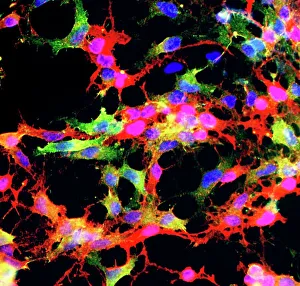
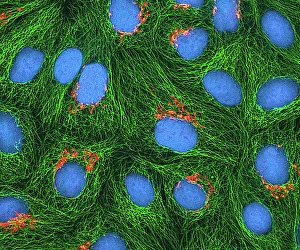
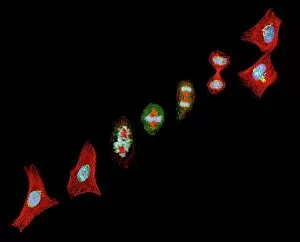
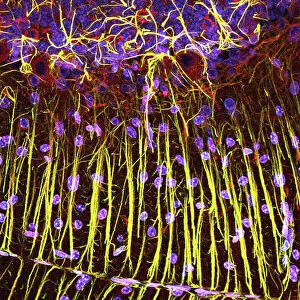
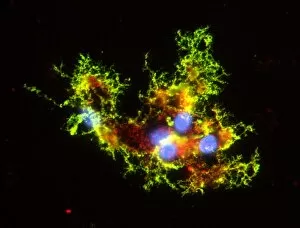
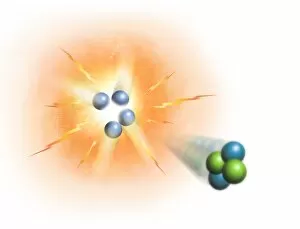
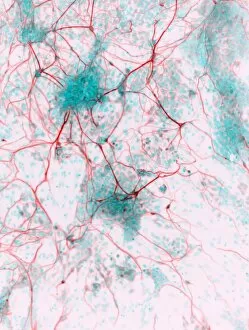
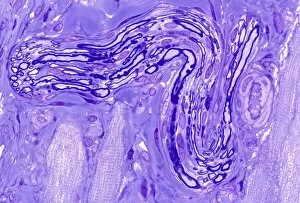
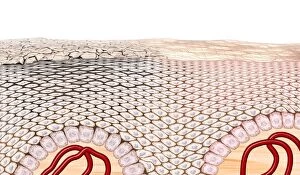
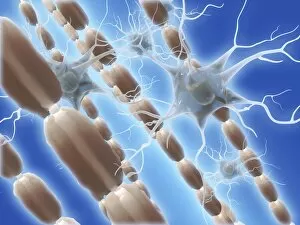
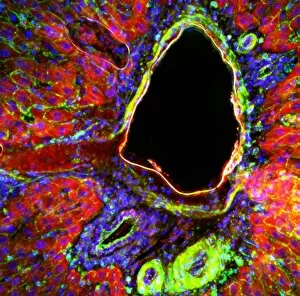
"Nuclei: The Intricate Powerhouses within Our Cells and Beyond" Delving into the microscopic world, we encounter the mesmerizing beauty of nuclei. In cerebellum tissue, a light micrograph reveals these vital command centers orchestrating our every move. Venturing deeper into scientific frontiers, we find ourselves at CERN's ATLAS detector, where nuclei play a crucial role in unraveling the mysteries of particle physics. Similarly, the CMS detector at CERN unveils their significance in understanding fundamental particles and forces. Shifting our focus to brain anatomy, hippocampus tissue showcases intricate nuclei that contribute to memory formation and spatial navigation. Meanwhile, HeLa cells captured under a light microscope exhibit their own unique nuclei patterns (C017 / 8299), highlighting their importance in medical research. Art meets science as an artwork depicting medulla oblongata reminds us of its critical role in regulating essential bodily functions through its specialized nuclei arrangement. Nuclear fission artwork further emphasizes how they are release immense energy when harnessed correctly. Zooming out to kidney tubules sectioned under a microscope slide unravels the presence of numerous cell nuclei responsible for maintaining fluid balance and waste elimination within our bodies. Expanding beyond traditional boundaries, glial stem cell culture offers insights into regenerative medicine with its vibrant display of proliferating nuclei (light micrograph). These versatile structures are central to cellular growth and differentiation processes. Examining cell structure more broadly uncovers how each nucleus houses genetic material that directs cellular activities like protein synthesis and DNA replication, and is this blueprint that shapes life itself. Lastly, exploring brain tissue blood supply highlights how oxygen-rich blood nourishes countless neuronal networks residing within diverse nuclear ensembles (HeLa cells - C017 / 8298). Intricate yet awe-inspiring, these glimpses into various realms remind us of the indispensable roles played by nucleic entities – from individual cells to complex systems – in shaping our understanding of life, physics, and medicine.