Myelin Collection
Myelin, a vital component of our nervous system, plays a crucial role in the transmission of nerve impulses
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
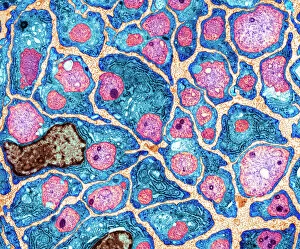
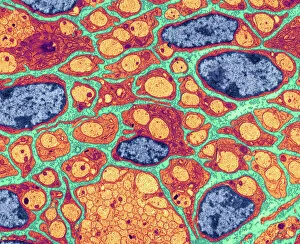
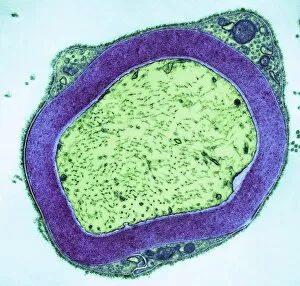
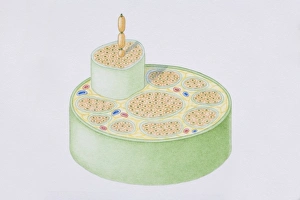
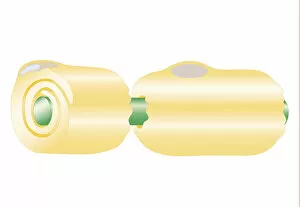
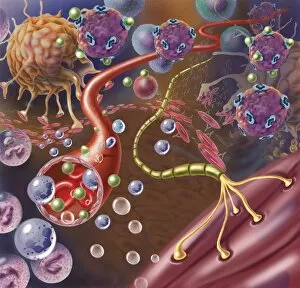
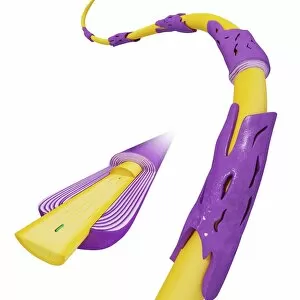
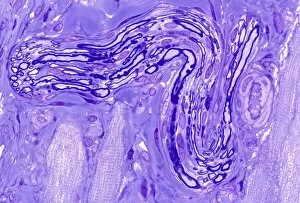
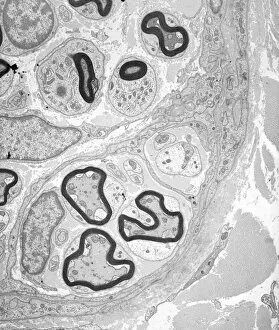
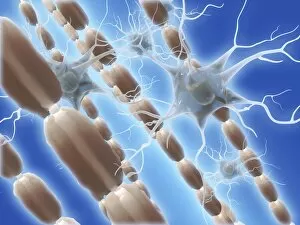
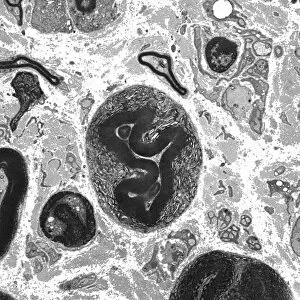
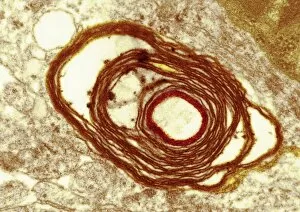
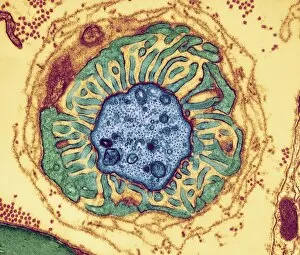
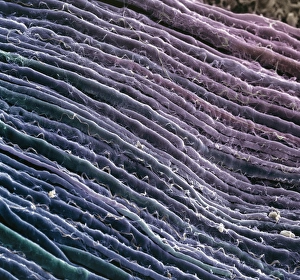
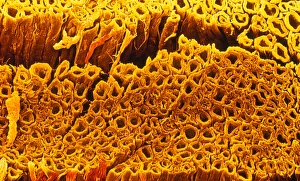
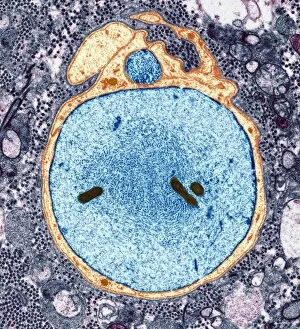
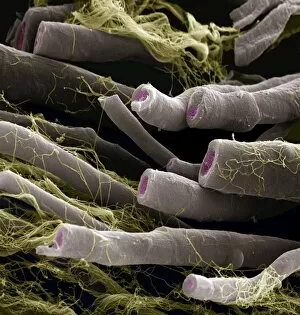
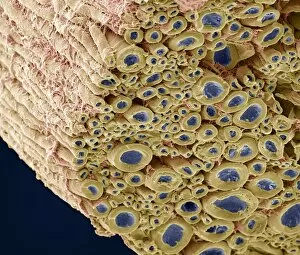
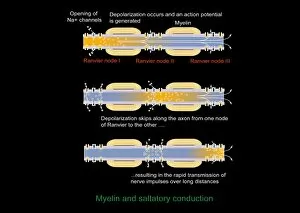
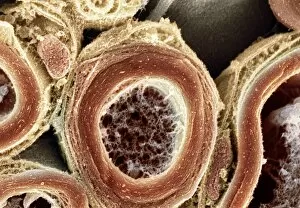
Myelin, a vital component of our nervous system, plays a crucial role in the transmission of nerve impulses. This fatty substance forms a protective and insulating sheath around nerve fibers, ensuring efficient communication between different parts of our body. Through the lens of a transmission electron microscope (TEM), we can observe the intricate myelination process. The TEM images reveal how myelin winds around axons, creating this essential sheath that shields and enhances signal conduction. In a cross-section diagram of a human nerve fascicle, we witness the complexity within peripheral nerves. Alongside bundles of nerve fibers, blood vessels intertwine with myelin sheaths to provide nourishment and support. Biomedical illustrations further illustrate the development and structure of nerves. In one image, myelin is depicted as sections wrapping around axons separated by Nodes of Ranvier—a critical feature for rapid impulse propagation. Another illustration showcases how myelin deteriorates over time, emphasizing its importance in maintaining proper neurological function. Light micrographs offer glimpses into real-life examples. A peripheral nerve captured under these microscopic lenses showcases individual fiber's myelinated nature—an exquisite network responsible for transmitting signals throughout our bodies. Similarly, an image depicting a nerve ganglion highlights the presence of both myelinated fibers and glial cells—essential components for optimal neural functioning. Lastly, it is fascinating to see how myelinated nerves connect with muscles through another light micrograph—the lower right corner revealing their integration into motor pathways that allow us to move effortlessly. Understanding the significance sheds light on various aspects related to our nervous system's health and functionality—a testament to its indispensable role in facilitating smooth communication within our bodies.