Molecular Graphic Collection
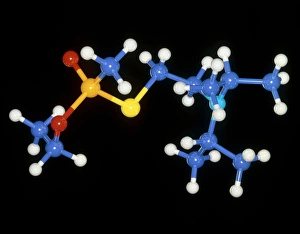
"Molecular Graphics: Unlocking the Intricacies of Life's Building Blocks" Witness the explosive intricacy of Sarin nerve gas molecules
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
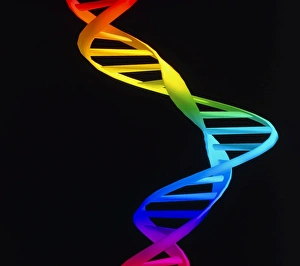
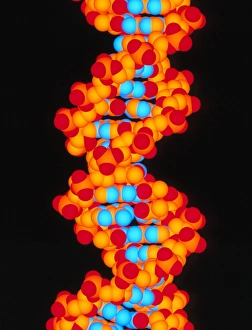
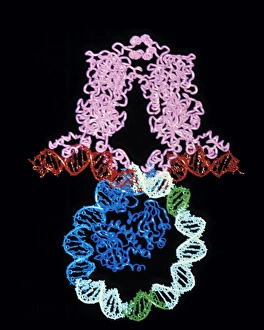
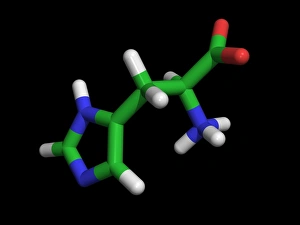
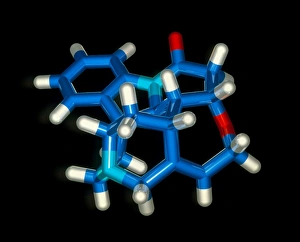
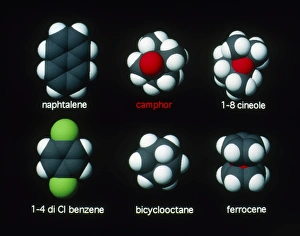
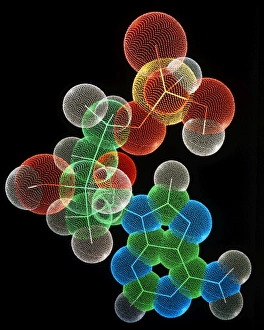
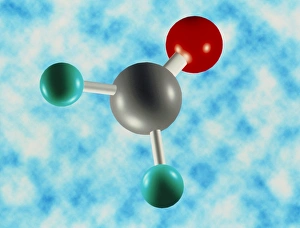
"Molecular Graphics: Unlocking the Intricacies of Life's Building Blocks" Witness the explosive intricacy of Sarin nerve gas molecules, unraveling their deadly secrets through molecular graphics. Dive into the microscopic world with a computer graphic showcasing the complex structure of ATP, the energy currency of life. Explore nature's vibrant palette as you delve into a stunning molecular graphic revealing the lycopene molecule responsible for tomato's rich red pigment. Marvel at an artistic representation of insulin, where science meets creativity to showcase this vital hormone's intricate molecular structure. Unleash your immune system superhero - Antibody. Discover its elegant architecture and understand how it fights off invaders through a captivating molecular graphic. Enter the realm of mechanical wonders with a computer model illustrating a universal joint, providing insights into its functionality and applications in various fields. Encounter one of humanity's most common foes – Rhinovirus – as you explore its detailed structure using cutting-edge molecular graphics technology. Embark on an extraordinary journey within our genetic blueprint by visualizing DNA helices in all their mesmerizing glory through advanced computer representations. Immerse yourself in awe-inspiring artwork unveiling part of a DNA molecule, capturing both its beauty and complexity simultaneously on screen. Witness scientific innovation at play as you examine a striking computer graphic highlighting deformities within DNA molecules, shedding light on potential genetic disorders or mutations. Behold the iconic double-helix structure that defines our very existence - DNA helix - portrayed vividly through state-of-the-art visualization techniques that bring this fundamental building block to life. Intricate and visually captivating, these remarkable molecular graphics offer us glimpses into worlds unseen; they serve as powerful tools for scientists to better comprehend life's mysteries while igniting curiosity among enthusiasts worldwide.