Microtubules Collection
Microtubules, the intricate cytoskeletal structures found in cells, play a vital role in various cellular processes
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
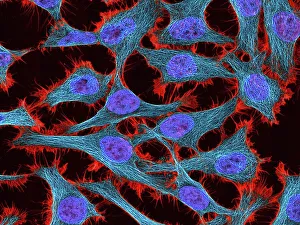
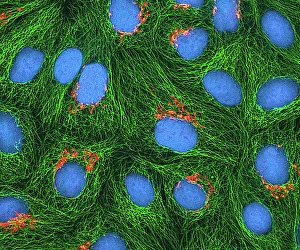
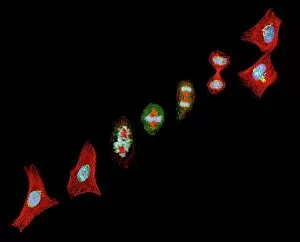
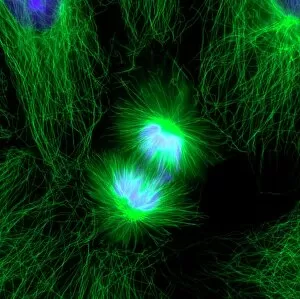
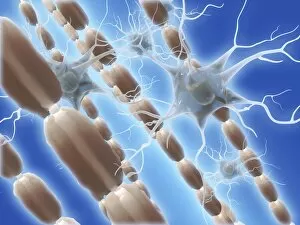
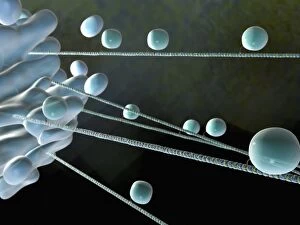
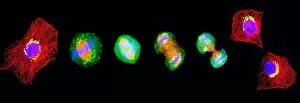
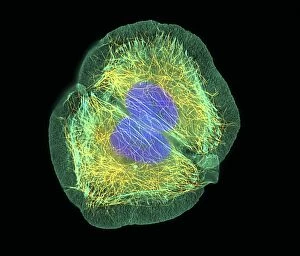
Microtubules, the intricate cytoskeletal structures found in cells, play a vital role in various cellular processes. In HeLa cells, as seen through light micrographs C017/8299 and C017/8298, these microscopic tubular structures are clearly visible. They form an essential part of mitosis, as depicted in the light micrograph showcasing cell division. Fluorescent micrographs capture the mesmerizing beauty of dividing cells and highlight the significance in this process. These fluorescent images provide a stunning glimpse into cell division and showcase how microtubules orchestrate this intricate dance. The structure of cells is intricately linked to microtubules. Plant cell mitosis can be observed through light microscopy, revealing how these tubular structures contribute to the formation of new plant cells. Not limited to just cellular division or structure maintenance, it also have diverse functions. Artwork C014/2646 showcases their association with myelin sheaths and glial cells – crucial components for proper nerve function. Illustration C018/0804 beautifully demonstrates how microtubule formation occurs within cells. This visual representation helps us understand the complex mechanisms behind their assembly and organization. Even sperm cells rely on microtubules for their motility and functionality. Artwork C018/6996 highlights their presence within sperm cells while TEM image C014/1463 zooms in on sperm tails where these tiny tubular structures are prominently displayed.