Macrophages Collection
Macrophages: The Artistry of Our Immune System In the intricate world of our immune system, macrophages stand as the artistic guardians
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
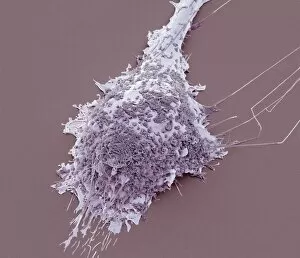
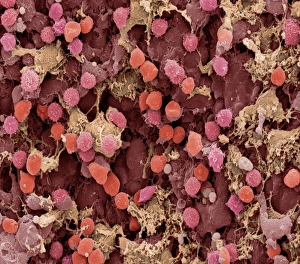
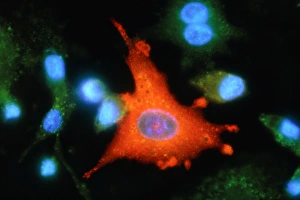
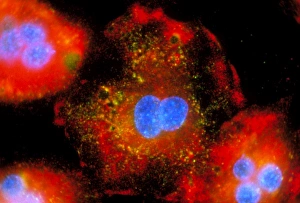
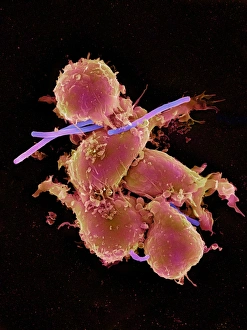
Macrophages: The Artistry of Our Immune System In the intricate world of our immune system, macrophages stand as the artistic guardians, diligently protecting our bodies from harm. These remarkable cells are like skilled painters, using their brushes to create a masterpiece that ensures our well-being. Dendritic cells play a crucial role in this process by capturing invaders and presenting them to macrophages for recognition. Together, they form an alliance against pathogens and foreign substances that dare to challenge our health. When we zoom into the microscopic realm, we witness the true beauty of these macrophage cells through powerful imaging techniques such as Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM). With its high resolution capabilities, TEM reveals intricate details of their structure – their elongated shapes resembling warriors ready for battle. But it is not just within tissues where these incredible defenders reside; even in our brains, microglial white blood cells take on the responsibility of safeguarding neural health. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) unveils mesmerizing images showcasing their unique morphology. From SEM C016 / 9115 to SEM C016 / 9119 and beyond, each image captures the elegance with which microglial white blood cells navigate through complex neural networks. The artistry continues as SEM C016 / 9109 showcases a solitary microglial cell amidst its surroundings - a reminder that even in isolation, these vigilant protectors remain steadfast in their duty. In contrast, SEM C016 / 9114 portrays multiple microglial white blood cells working together harmoniously towards one common goal: preserving brain homeostasis. As we delve deeper into this captivating gallery of images - SEM C016 / 9113 displays clusters of interconnected microglia while SEM C016 / 9118 highlights individuality among them - we realize how intricately woven this artwork truly is.