Liver Cell Collection
The liver cell, also known as a hepatocyte, plays a crucial role in maintaining our overall health
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
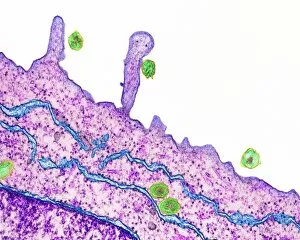
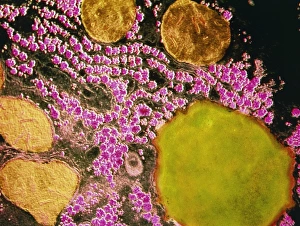
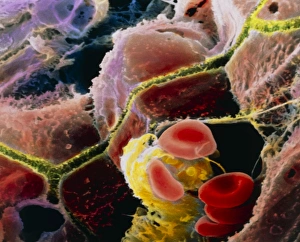
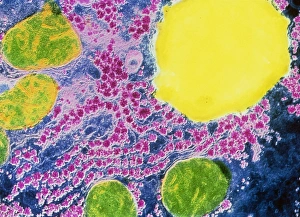
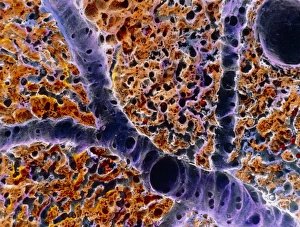
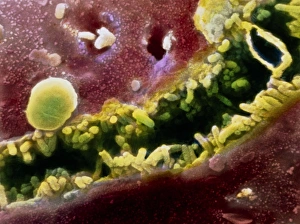
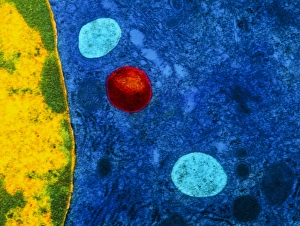
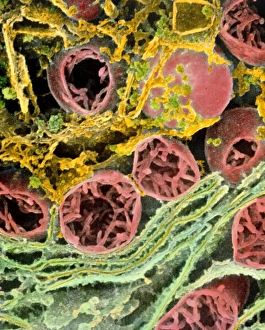
The liver cell, also known as a hepatocyte, plays a crucial role in maintaining our overall health. These remarkable cells are involved in various processes that keep our body functioning optimally. One significant challenge faced by liver cells is the invasion of Hepatitis C viruses. Through the use of Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM), scientists have been able to observe these tiny viral particles interacting with hepatocytes at an incredibly detailed level. Another essential organelle found within liver cells is the Golgi apparatus. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) has allowed researchers to visualize this complex structure and understand its role in processing and packaging proteins for secretion. In a False-colour TEM image of a human hepatocyte, we can appreciate the intricate network of cellular components that make up these vital cells. The image showcases their unique morphology and highlights specific organelles such as mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum. Coloured SEM images provide us with an even more vivid representation of liver cells and their surrounding environment. In one striking image, we can see liver cells along with bile canaliculi - small ducts responsible for transporting bile produced by hepatocytes. A section through a liver cell captured using False-colour TEM reveals further details about its internal structure. This high-resolution image allows us to study different compartments within the cell, including nuclei and cytoplasmic components like ribosomes. Within each lobule of the liver lies an intricate network of vessels that ensure proper blood supply for metabolic functions. A captivating False-colour SEM image beautifully illustrates this vascular system within a liver lobule. When observed under light microscopy, individual hepatocytes appear as distinct polygonal shapes forming tissue patterns characteristic of healthy livers. This light micrograph provides valuable insights into their arrangement within hepatic tissue sections. An illustration depicting the structure of a human hepatocyte offers an informative overview highlighting key features such as nuclei, mitochondria, Golgi apparatus, and rough endoplasmic reticulum.