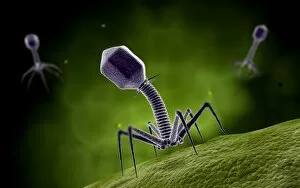
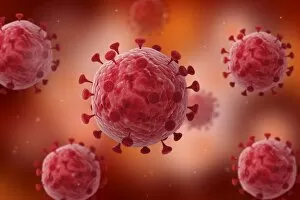
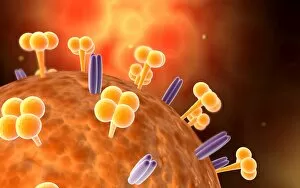
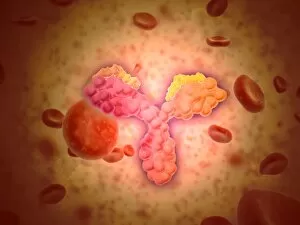
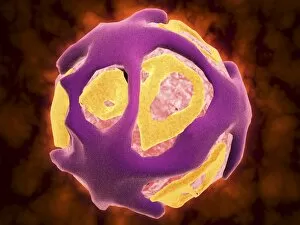
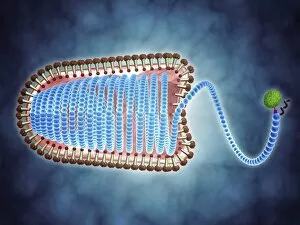
Infection Collection (page 13)
"Infection: A Historical Journey into the Battle against Disease" In the realm of medicine, it has long been a formidable adversary
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
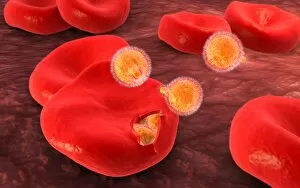
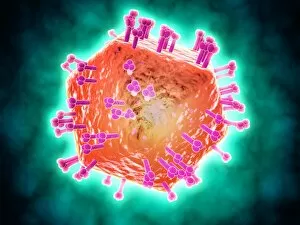
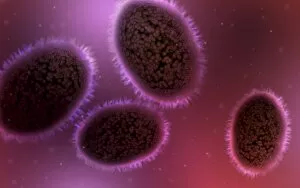
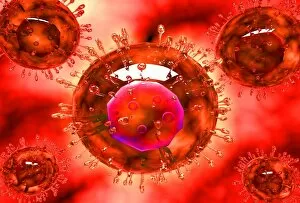
"Infection: A Historical Journey into the Battle against Disease" In the realm of medicine, it has long been a formidable adversary. From ancient plagues to modern epidemics, humanity has faced countless battles against unseen foes that threaten our very existence. This caption takes us on a captivating journey through history, exploring various artworks and moments that shed light on the fight against infectious diseases. The Cow-Pock satirical etching by James Gillray in 1802 introduces us to Edward Jenner and his groundbreaking work on vaccination. This pivotal moment marked a turning point in medical history, as Jenner's discovery paved the way for immunization practices that would save countless lives. Moving further back in time, we encounter an eerie 17th-century artwork depicting a plague doctor. These haunting figures were tasked with treating victims during one of history's most devastating pandemics - the Black Death. Their iconic beaked masks and dark robes serve as chilling reminders of the horrors unleashed by infectious diseases. Fast forward to 1866, where Deaths Dispensary cartoon highlights water pollution as a source of disease. This powerful image serves as a stark reminder of how environmental factors can contribute to widespread infections and emphasizes the importance of clean water for public health. Another striking woodcut from London during the Great Plague of 1665 begs for divine intervention: "Lord, have mercy on London. " The desperation felt during this catastrophic event is palpable even centuries later, reminding us of our vulnerability when faced with rampant infections. Shifting gears to Cuba in c1900, we witness Dr. Carlos Finlay and Dr. Walter Reed leading efforts against yellow fever after the Spanish-American War. The oil painting captures their determination alongside other physicians observing inoculation procedures – showcasing bravery amidst uncertainty while combating deadly outbreaks. Calots spinal surgery illustration from the 19th century showcases medical advancements aimed at tackling specific infections affecting vital organs like tuberculosis or addressing conditions requiring surgical intervention such as spinal disorders.