Hepatocyte Collection
A hepatocyte, also known as a liver cell, is a vital component of the liver tissue
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
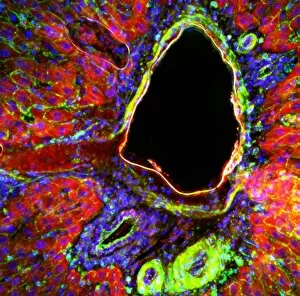
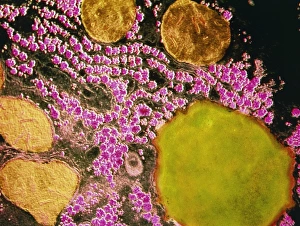
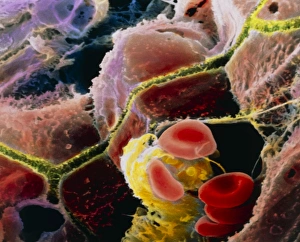
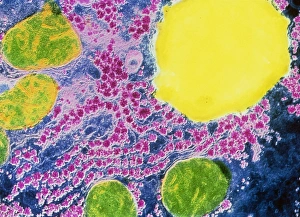
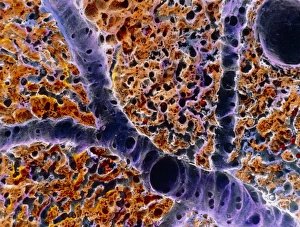
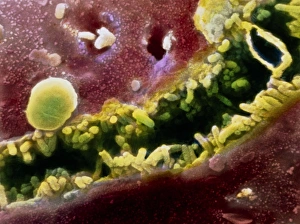
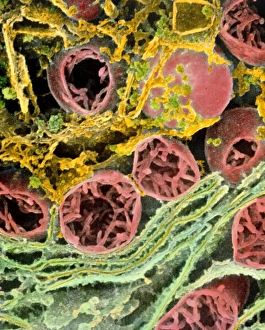
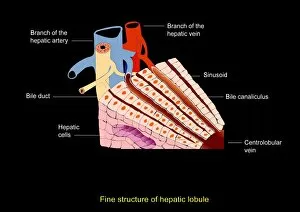
A hepatocyte, also known as a liver cell, is a vital component of the liver tissue. These specialized cells play a crucial role in maintaining the overall health and functionality of this essential organ. Under the powerful lens of a transmission electron microscope (TEM), one can observe the intricate laminae formed by hepatocytes. These layers create an organized structure within the liver tissue, allowing for efficient functioning. Unfortunately, certain conditions like cirrhosis can affect these remarkable cells. In light micrographs depicting cirrhosis of the liver, one can witness the detrimental impact on hepatocytes. The images reveal distorted and damaged cells that are unable to perform their duties effectively. In TEM images showcasing liver tissue affected by cirrhosis, further details emerge about how this condition disrupts normal cellular architecture. The once-organized arrangement becomes disrupted and irregular due to fibrosis and scarring caused by chronic inflammation. The importance of understanding hepatocytes' structure extends to studying liver portal triads - areas where hepatic arteries, bile ducts, and hepatic veins converge. Light micrographs provide insights into these complex structures within healthy liver tissue. To gain even more insight into hepatocyte morphology at a microscopic level, false-color TEM images offer enhanced visualization. These vibrant representations allow researchers to study various components within these cells with greater clarity. Additionally, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) provides colored views of both hepatocytes and bile canaliculi - small channels through which bile flows within the liver. This technique helps researchers examine not only individual cells but also their interconnections in detail. By combining different imaging techniques such as TEM and SEM with traditional light microscopy approaches, scientists continue to unravel mysteries surrounding hepatocytes' functions and dysfunctions alike. Understanding these fundamental units is crucial for developing treatments targeting diseases affecting this vital organ system.