Erythrocytes Collection
Erythrocytes, commonly known as red blood cells, play a vital role in our body's functions
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
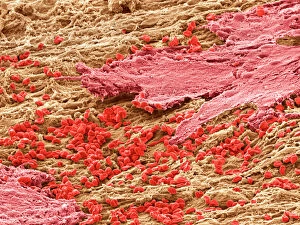
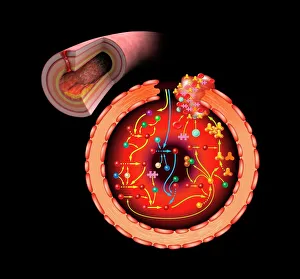
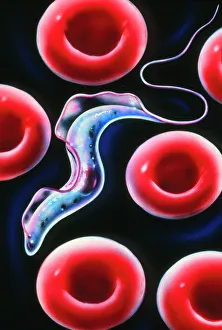
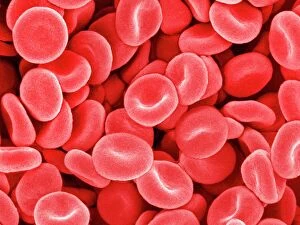
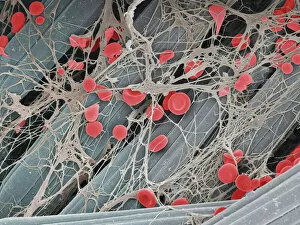
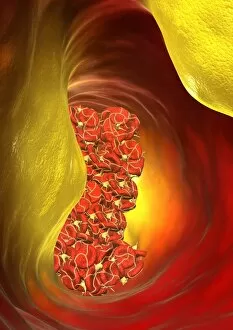
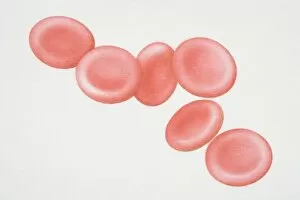
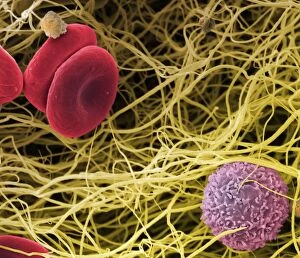
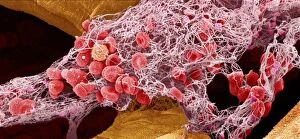
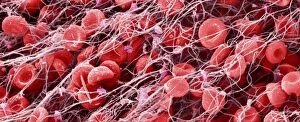
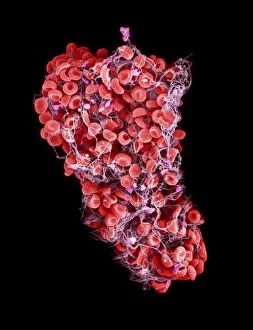
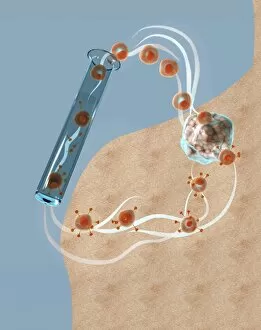
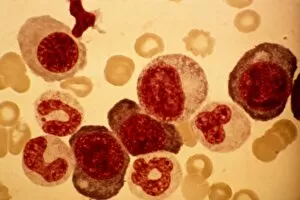
Erythrocytes, commonly known as red blood cells, play a vital role in our body's functions. These microscopic wonders are responsible for carrying oxygen to every cell and removing carbon dioxide waste. During menstruation, the lining of the uterus sheds, causing bleeding. Erythrocytes work tirelessly to transport oxygen-rich blood to this area, aiding in the healing process. In intricate SEM (scanning electron microscope) images, we can witness the beauty of these blood cells up close. Their unique shape allows them to squeeze through narrow capillaries and reach even the tiniest corners of our bodies. The blood coagulation cascade is another fascinating aspect involving erythrocytes. Artwork C016 / 9873 showcases this complex process where platelets and clotting factors interact with red blood cells to form clots that prevent excessive bleeding when we get injured. SEM images also reveal red and white blood cells side by side – an army working together to defend us against infections and diseases. It's incredible how these tiny warriors fight off invaders while maintaining harmony within our bloodstream. Sometimes things go awry; parasites like those causing sleeping sickness or mouse malaria invade erythrocytes, disrupting their normal function. SEM imagery helps scientists study these pathogens' behavior inside our precious red blood cells so they can develop effective treatments. Blood clot formation is crucial for wound healing but can also pose risks if it occurs abnormally within vessels or organs. SEM image C016 / 9747 captures a detailed view of a clot on plaster – reminding us of both its importance and potential complications. Computer artwork beautifully illustrates the structure alongside other components like plasma proteins or heart muscles - showcasing their interconnectedness within our circulatory system. Erythrocytes truly deserve admiration for their tireless efforts in keeping us alive and healthy.