Clotting Collection
"Unraveling the Intricate Dance of Clotting
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
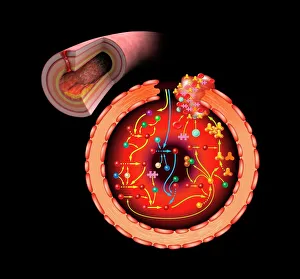
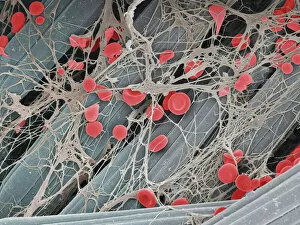
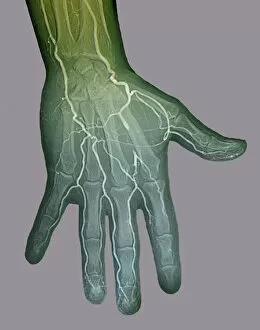
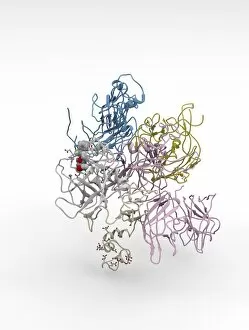
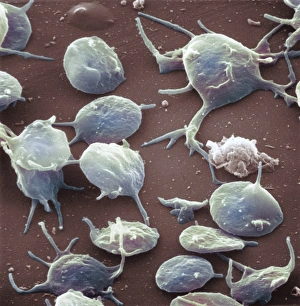
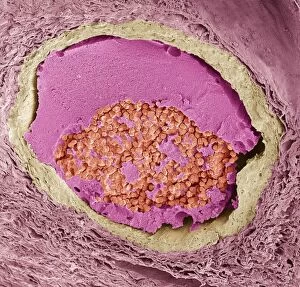
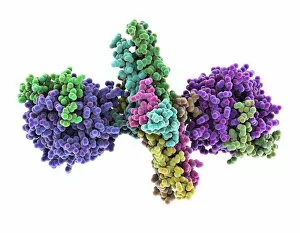
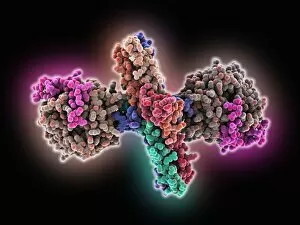
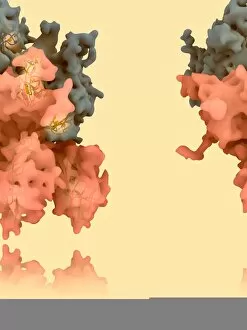
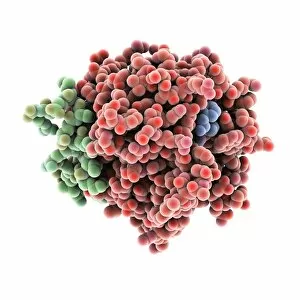
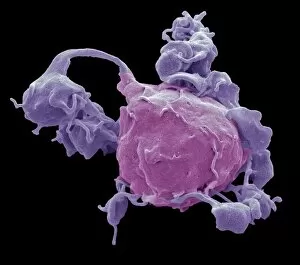
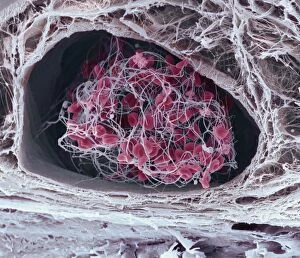
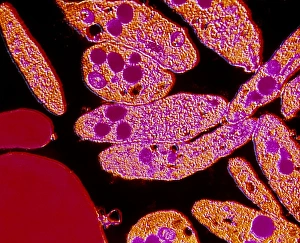
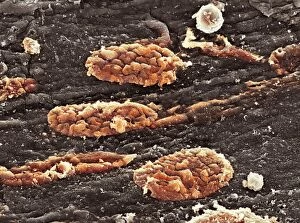
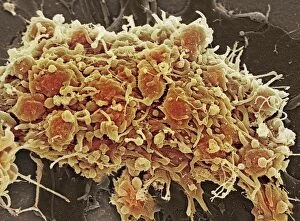
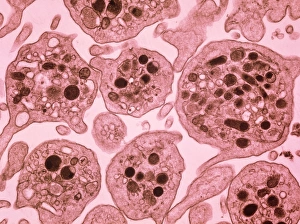
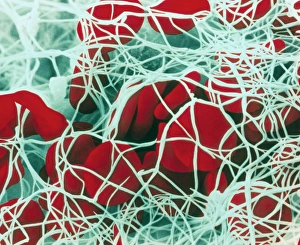
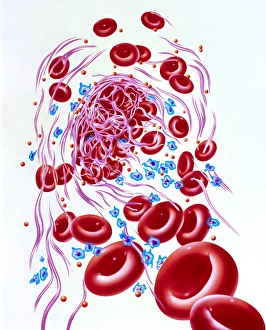
"Unraveling the Intricate Dance of Clotting: Exploring the Blood Coagulation Cascade" Intriguing artwork C016 / 9873 takes us on a visual journey into the complex process of blood clotting. Liver cirrhosis, a condition that affects liver function, can disrupt this delicate balance and lead to abnormal clot formation. SEM images reveal the intricate structure of a blood clot on plaster (Blood clot on plaster, SEM) and offer a closer look at individual platelets coming together to form a solid mass (Platelets, SEM). Ischaemia is captured in stunning detail through digital angiogram imagery (Ischaemia, digital angiogram), showcasing how inadequate blood flow can result in tissue damage due to insufficient oxygen supply. Artwork C016 / 4619 beautifully illustrates the formation of a blood clot as it obstructs normal circulation within our bodies. SEM images C016 / 3099 and C016 / 3098 provide captivating glimpses into the collaboration between white blood cells and platelets during coagulation - an essential defense mechanism against excessive bleeding. The coagulation factor complex molecule (Coagulation factor complex molecule C014 / 0139) plays a crucial role in orchestrating this intricate dance by activating various proteins involved in clot formation. Thrombosed blood vessels are brought to life through artwork C013 / 4649, emphasizing their potential consequences if left untreated or unmanaged. Finally, SEM image P260 / 0123 showcases another mesmerizing close-up view of a formed blood clot – highlighting its unique composition and structure. Through these captivating visuals and scientific insights, we gain deeper appreciation for the remarkable phenomenon known as "clotting, " which safeguards our bodies from excessive bleeding while reminding us of its critical importance in maintaining overall health.