Adenine Collection
Adenine, a fundamental building block of life, plays a crucial role in the genetic code
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
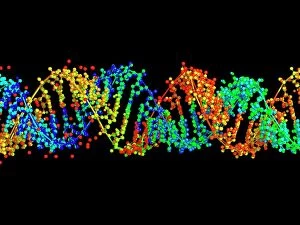
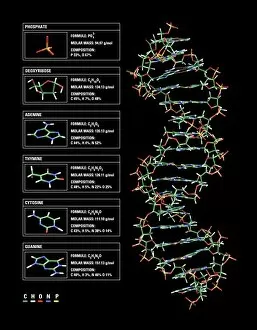
Adenine, a fundamental building block of life, plays a crucial role in the genetic code. As part of a double-stranded RNA molecule or DNA molecule, adenine pairs with thymine (in DNA) or uracil (in RNA), forming the bonds that hold our genetic information intact. Its significance is beautifully depicted in artwork showcasing the intricate structure of DNA. In recent years, it has been at the forefront of scientific breakthroughs. From grapevine genome sequencing to unraveling complex diseases, researchers have relied on this remarkable molecule to unlock nature's secrets. The grapevine genome sequencing project utilized adenine's presence within DNA molecules to decode and understand its unique characteristics. Artwork depicting the elegant structure of DNA highlights adenine as one of its key components. With its distinct shape and chemical properties, it symbolizes both complexity and simplicity simultaneously—a testament to nature's genius. Conceptual images further emphasize adenine's importance by representing it as an integral part of the iconic double helix structure. These captivating visuals remind us that every living organism carries their own version of this essential molecule within their cells. As we delve deeper into genetics and explore new frontiers in medicine and biotechnology, adenine remains an indispensable piece in deciphering life's mysteries. It serves as a reminder that even on a microscopic level, there is beauty and wonder waiting to be discovered—each strand holding countless possibilities for understanding ourselves and our world better.