Water Clock Collection
The water clock, also known as a clepsydra, has a rich history dating back to ancient times
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
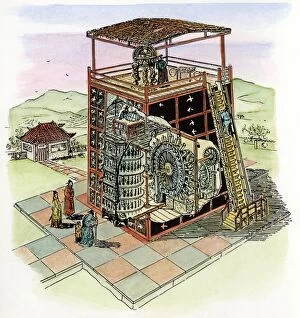
The water clock, also known as a clepsydra, has a rich history dating back to ancient times. One notable reconstruction is that of the clepsydra invented by Ctesibius of Alexandria around 270 BC. This remarkable invention allowed people to measure time using the flow of water. In an illustration from Les Raisons des Forces Mouvantes, we get a glimpse into how this ingenious device worked. The intricate mechanisms and gears are depicted in great detail, showcasing the brilliance of its design. An old copperplate engraving showcases another version of the clepsydra, highlighting its timeless appeal. The black and white photo adds a touch of nostalgia to this ancient timekeeping instrument. Moving on to Athens, we encounter The Tower of Winds in the Roman agora. This impressive structure not only served as a water clock but also featured sundials and weather vanes. Its reconstruction gives us insight into how our ancestors measured time with precision and accuracy. Traveling across continents brings us to India's Palace of Bundi where an ancient they are be found. Captured in black and white photography, it exudes an air of mystery and grandeur. Rome's Pincian Hill offers yet another glimpse into the world of water clocks with Clepsydra Orologio ad Acqua located within Villa Borghese Gardens. This picturesque setting provides an enchanting backdrop for this historical marvel. Heading back to Athens once again, we encounter The Tower Of Winds from the first century AD. Its elegant architecture stands tall against the test of time while reminding us of humanity's quest for measuring time accurately. Egyptian culture also embraced water clocks as evidenced by their own unique designs showcased in various artifacts throughout history. These captivating pieces give us a window into their sophisticated understanding and appreciation for keeping track of time. One particularly fascinating example is an intricately designed clepsydra indicating hours and chiming bells created between 1617-1619.