Vagus Nerve Collection
"The Vagus Nerve: Unraveling the Intricacies of the Human Brain's Communication Highway" The vagus nerve, also known as cranial nerve X
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
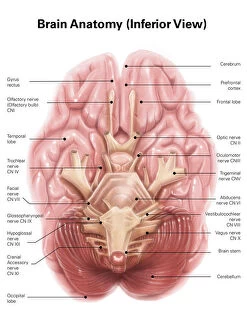
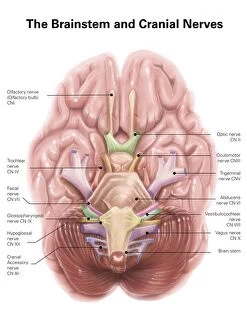
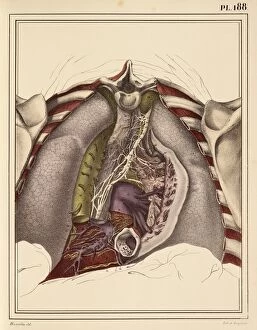
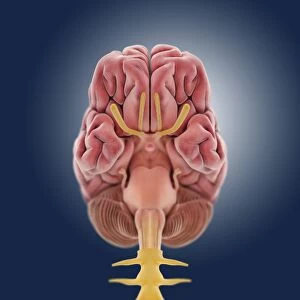
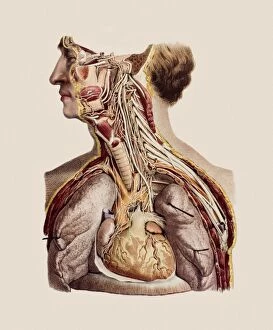
"The Vagus Nerve: Unraveling the Intricacies of the Human Brain's Communication Highway" The vagus nerve, also known as cranial nerve X, is a vital component of the human nervous system. Situated deep within the anatomy of the human brain, this intricate network plays a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions. When we examine the inferior view of the human brain, its complexity becomes apparent. The artwork C018/0300 beautifully illustrates how this nerve intertwines with other nerves and structures to form an elaborate web-like pattern. As part of the cranial nerves, it extends beyond just our brain and into our body. It connects to numerous organs such as lungs and liver through branches like pulmonary nerve plexus and liver portal triad respectively. These connections highlight its significance in maintaining homeostasis throughout our entire physiology. Moreover, understanding tongue anatomy helps us comprehend how this nerve influences speech and swallowing mechanisms. Its involvement in these processes showcases its importance not only for physical well-being but also for effective communication. Furthermore, illustrations depicting cervical lymph nodes shed light on another aspect function - its role in immune response regulation. This connection between our nervous system and immune system highlights how intricately intertwined different systems are within our bodies. The vagus nerve serves as a bridge between mind and body by transmitting signals bidirectionally. It relays information from internal organs to our brain while simultaneously sending instructions back to those organs for proper functioning. Studying this remarkable neural pathway allows scientists to gain insights into treating various disorders such as epilepsy or depression through techniques like vagal stimulation therapy. Exploring the vast realm anatomy reveals its indispensable contribution to overall health and well-being. From being an integral part of brainstem structure to influencing multiple organ systems, it truly exemplifies nature's brilliance in designing complex networks that govern human existence.