Tubules Collection
"Tubules: The Intricate World of Cellular Structures" In the vast realm of biology, tubules play a crucial role in various organisms
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
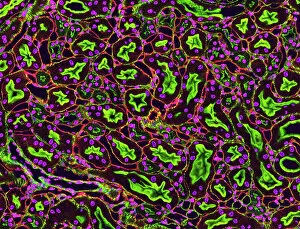
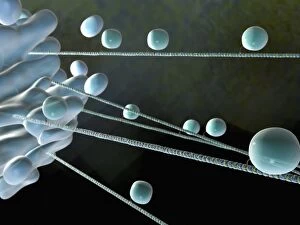
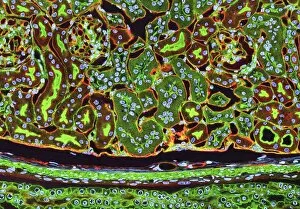
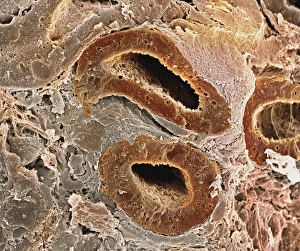
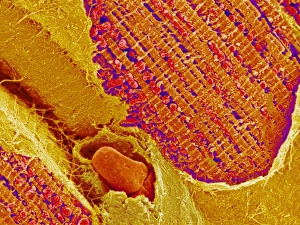
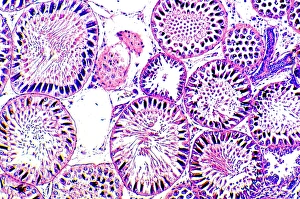
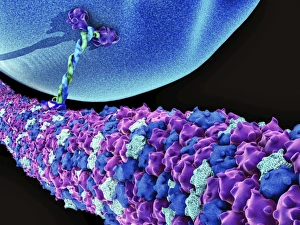
"Tubules: The Intricate World of Cellular Structures" In the vast realm of biology, tubules play a crucial role in various organisms. Kidney tubules, for instance, are intricate sections within this vital organ that aid in the filtration and reabsorption processes. These tiny structures ensure the balance of fluids and electrolytes within our bodies. Proteins also rely on microtubules to navigate through cells, acting as highways for intracellular transport. Fascinating artwork captures this complex system, showcasing the beauty hidden within our own bodies. But tubules aren't limited to human anatomy alone; they exist across different species. Take the light-sensitive Sea Cucumber (Holothuria impatiens), which defends itself by extruding sticky cuvierian respiratory tubules when threatened. Similarly, the Brown Sandfish Sea Cucumber (Bohadschia vitiensis) deploys white sticky cuvierian tubules as its defensive mechanism. Fluorescence micrographs provide us with mesmerizing glimpses into kidney tissue's inner workings. These images reveal an intricate network of interconnected tubular structures responsible for maintaining our body's equilibrium. Artwork depicting intracellular transport showcases how essential these microscopic tubes are in ensuring proper cellular function. They act as conduits for molecules and organelles to move seamlessly throughout cells, enabling efficient communication and coordination. Sea cucumbers continue to amaze us with their unique abilities. At nightfall, adult specimens like Holothuroidea sp. , Bohadschia argus, or Bohadschia vitiensis can be seen extruding white sticky respiratory tubules during defensive actions. This remarkable display serves as a reminder of nature's ingenuity and adaptability. From kidneys to sea cucumbers, from fluorescence micrographs to stunning artwork - all these examples highlight just how significant tubular structures are in shaping life on Earth. Their presence underscores both complexity and elegance within biological systems, leaving us in awe of the wonders that lie beneath the surface.