Tubule Collection
"Tubule: The Intricate Network of Excretion and Function in Our Body" The kidney tubules, when observed in section
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
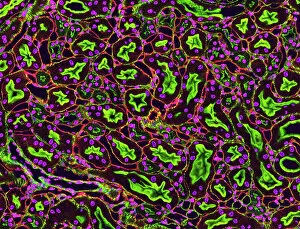
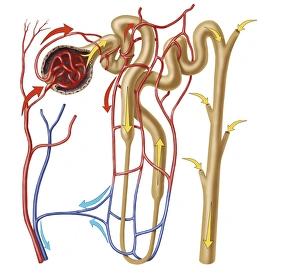
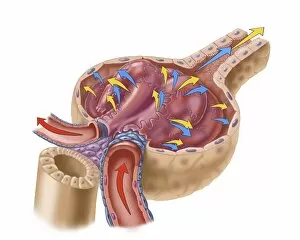
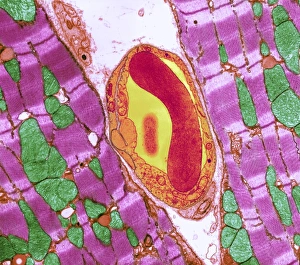
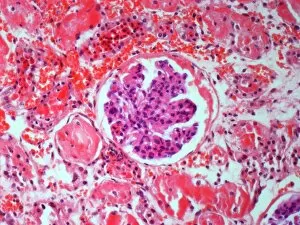
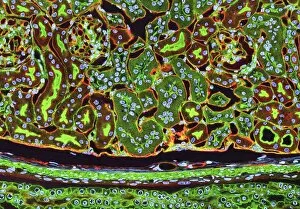
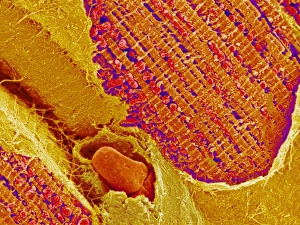
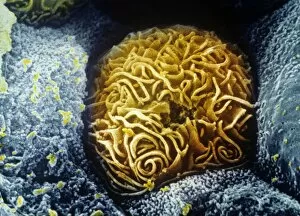
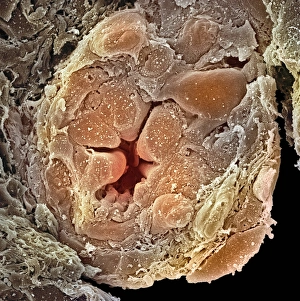
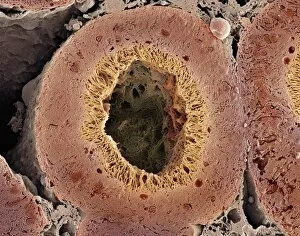
"Tubule: The Intricate Network of Excretion and Function in Our Body" The kidney tubules, when observed in section, reveal the remarkable complexity of the nephron - the functional unit responsible for excretion within our human kidneys. These tiny structures play a crucial role in maintaining our body's equilibrium. Intriguingly, a TEM image showcases the intricate arrangement of cardiac muscle cells, highlighting their interconnections. Another TEM image captures the close proximity between cardiac muscle and capillaries, emphasizing their vital relationship for efficient oxygen supply. Artwork depicting the nephron structure provides an insightful glimpse into its anatomy. This complex system consists of various components working harmoniously to filter waste products from our blood while retaining essential substances like water and electrolytes. A microscopic view reveals dentine with its unique composition and structure. This dental tissue forms an integral part of our teeth, providing strength and protection against external forces. A conceptual image showcasing the cytoskeleton offers a visual representation of this dynamic network within cells. It plays a pivotal role in maintaining cell shape, facilitating movement, and supporting cellular functions. The renal glomerulus is another critical component involved in filtration processes within the kidney. Its intricate architecture ensures effective removal of waste materials while preserving valuable molecules required by our body. Anatomy exploration further unravels Bowman's glomerular capsule - an essential part that encapsulates the glomerulus. Understanding its structure aids comprehension of how filtration occurs efficiently within this specialized region. Once again, we encounter a conceptual image illustrating the significance of cytoskeletons – these internal scaffolds provide structural support to maintain cell integrity across diverse tissues throughout our bodies. Lastly, examining a microscopic cross-section view unveils fascinating details about small intestine physiology. This highly specialized organ absorbs nutrients from digested food through its extensive network of tubules called villi – ensuring optimal nutrient uptake for sustaining bodily functions.