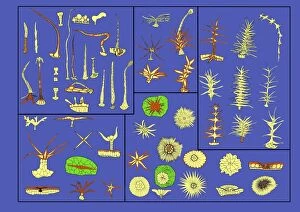
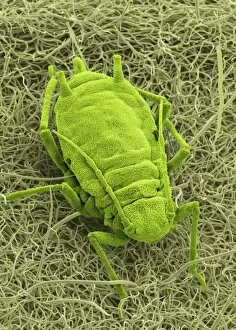
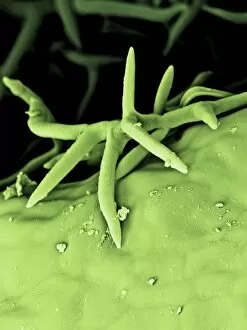
Trichomes Collection
Trichomes are tiny structures found on the surfaces of various plants, serving a multitude of functions. Take for instance the Botanik Digitalis purpurea L
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
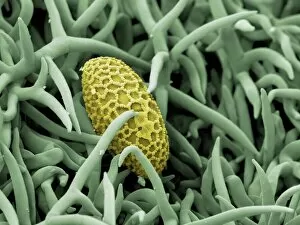
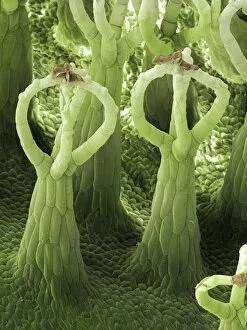
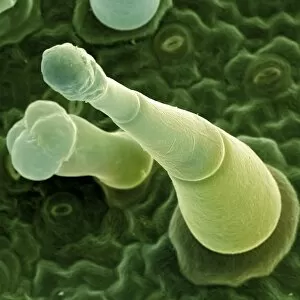
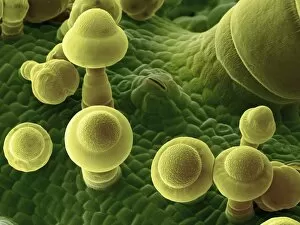
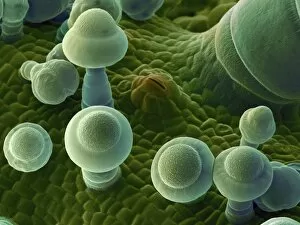
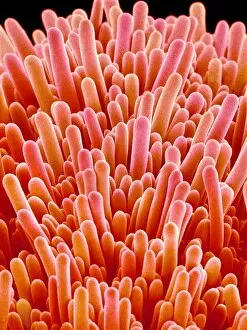
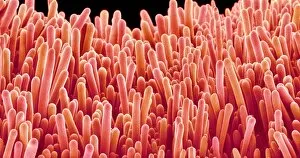
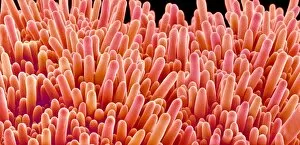
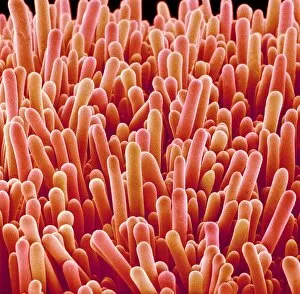
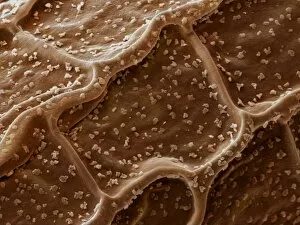
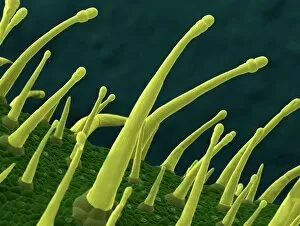
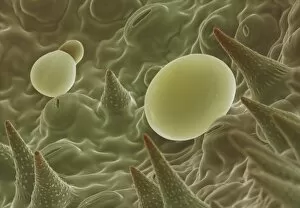
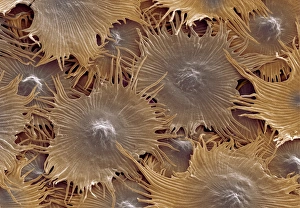
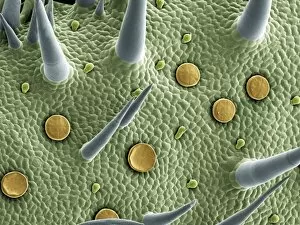
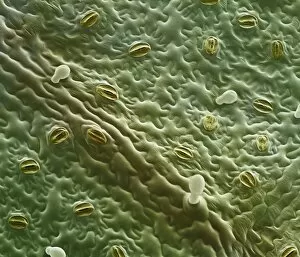
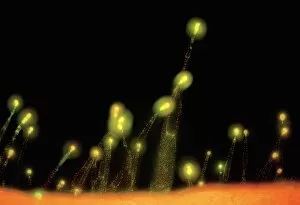
Trichomes are tiny structures found on the surfaces of various plants, serving a multitude of functions. Take for instance the Botanik Digitalis purpurea L. Fingerhut 160:1 trichome, which can be observed under scanning electron microscopy (SEM). These trichomes appear as delicate hairs on the leaf surface of French lavender, creating a stunning visual display. Moving on to another SEM image, we explore an Aubergine flower petal's intricate trichome structure. Each petal is adorned with these microscopic projections that provide protection and aid in pollination. In contrast, Lily pollen grains delicately rest upon a rosemary leaf's surface, showcasing how they are act as landing platforms for reproductive particles. Gorse flower buds also possess their own unique trichome arrangement when viewed through SEM. These fine hairs contribute to the plant's defense mechanism against herbivores and harsh environmental conditions. Leaf oil glands offer yet another fascinating example of trichomes' diversity. Under SEM examination, these glandular structures reveal themselves as small reservoirs responsible for producing essential oils that give plants their distinct aromas and potential medicinal properties. Returning to French lavender leaves once more, we witness an enchanting spectacle through SEM imaging. The intricate network covering each leaf creates a textured landscape reminiscent of miniature forests. Periwinkle petals exhibit their own captivating array of trichome patterns when examined under SEM. These hair-like structures add texture and beauty to the already vibrant flowers they adorn. Nettle leaves showcase yet another type of intriguing trichome structure under close scrutiny by SEM technology. These stinging hairs serve as protective mechanisms against herbivores or unsuspecting passersby who may brush against them unknowingly. Orchid petals present an exquisite sight when magnified using SEM techniques.