Theory Collection (page 7)
"Theory: Unveiling the Hidden Patterns of the Universe" From ancient times to modern scientific breakthroughs, theories have shaped our understanding of the world
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
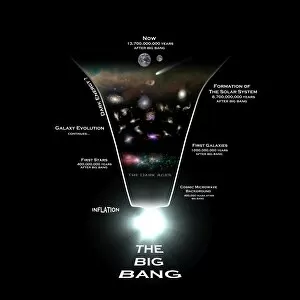
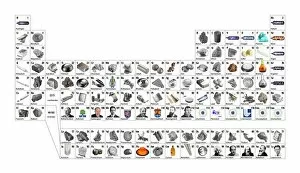
"Theory: Unveiling the Hidden Patterns of the Universe" From ancient times to modern scientific breakthroughs, theories have shaped our understanding of the world. A histological diagram of a mammalian retina reveals intricate structures that support the theory of vision. Mendeleyev's periodic table, created in 1869, laid the foundation for understanding elements and their properties. Richard Feynman, a brilliant physicist depicted in a caricature, contributed to quantum mechanics and explained complex concepts with his unique approach. The standard periodic table showcases various element types discovered over centuries. The bust of Claudius Galen reminds us of his influential medical theories during ancient Rome. An artwork depicting the universe timeline takes us on an awe-inspiring journey through cosmic evolution. A geological unconformity on the river Jed hints at Earth's dynamic nature and supports theories about plate tectonics. Starlight bent by the Sun's attraction highlights Einstein's theory of general relativity, revolutionizing our perception of gravity. Dalton's table of atomic symbols from 1835 provides insights into early attempts to understand matter at its fundamental level. Continental drift maps demonstrate how continents have shifted over millions of years due to plate tectonics. The concept of multiple universes challenges conventional thinking and expands our imagination beyond what we can observe directly. Theories continue to push boundaries and inspire new discoveries as humanity strives to unravel the mysteries surrounding us. In this captivating collage, we witness how theories connect seemingly disparate fields - from biology and chemistry to physics and geology - offering glimpses into profound truths that shape our existence in this vast universe.