Telencephalon Collection
The telencephalon, also known as the cerebral hemispheres, is a fascinating part of the human brain
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
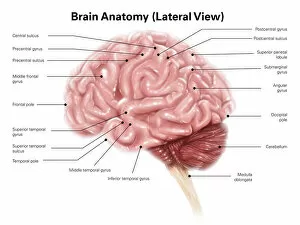
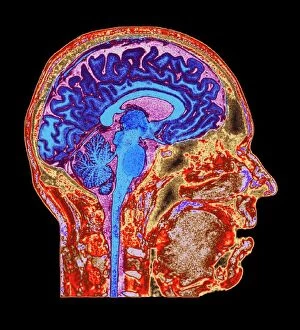
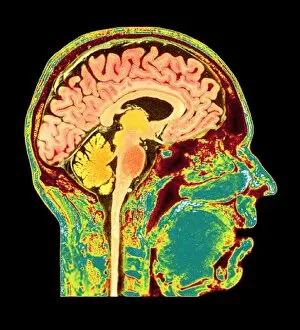
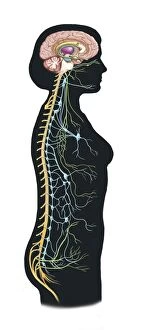
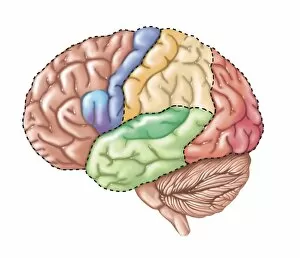
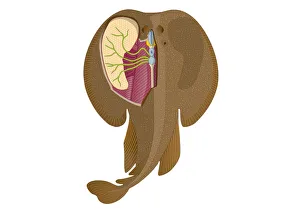
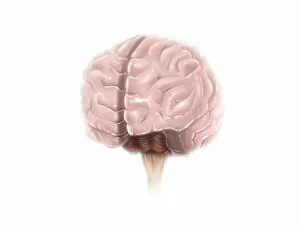
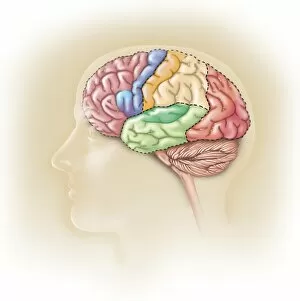
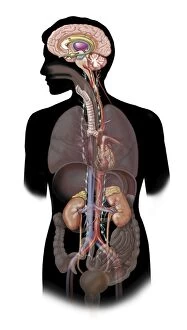
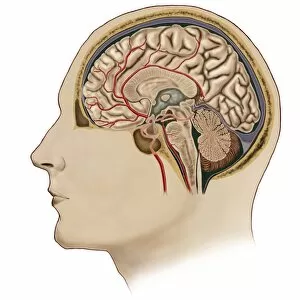
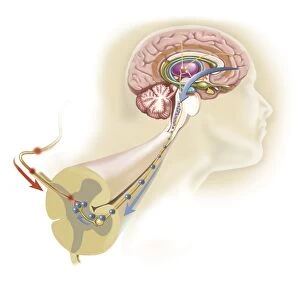
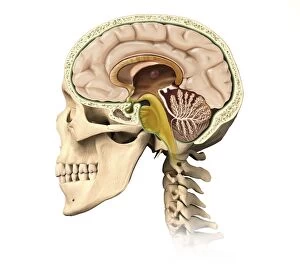
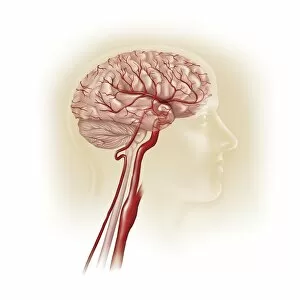
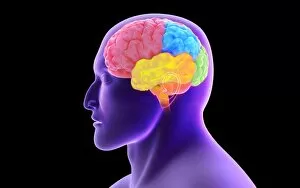
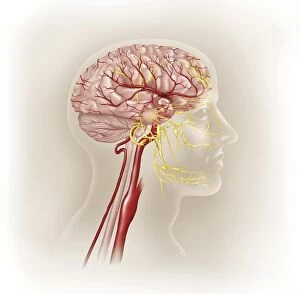
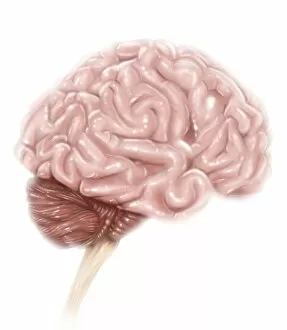
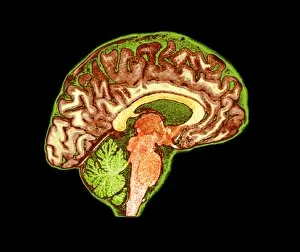
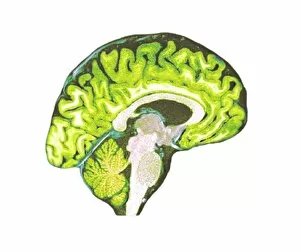
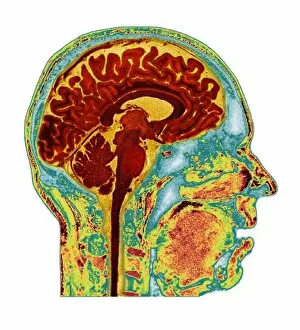
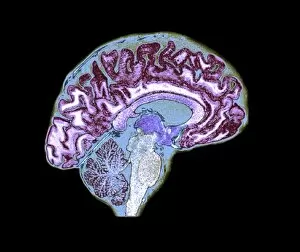
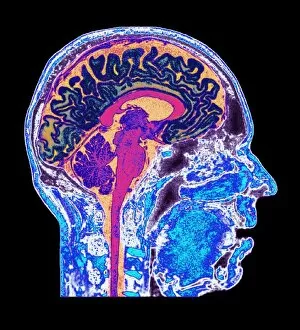
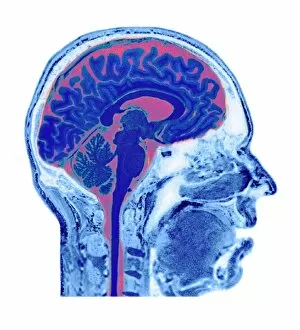
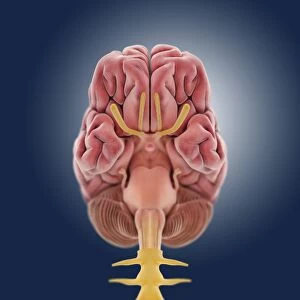
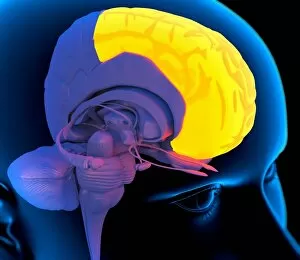
The telencephalon, also known as the cerebral hemispheres, is a fascinating part of the human brain. In this captivating image, we are presented with a lateral view of the telencephalon in all its intricate glory. The MRI scans C016/8845, C016/8850, and C016/8843 provide us with detailed visuals of a normal human brain. As we delve deeper into understanding this complex organ, we discover that it plays an integral role in our autonomic nervous system and limbic system. This connection between our body's involuntary functions and emotions highlights the significance of the telencephalon in regulating our responses to various stimuli. Examining the surface anatomy of the brain reveals labeled structures that aid in comprehending its functionality. Additionally, observing a side view allows us to identify different lobes responsible for specific cognitive processes. Intriguingly, even during fetal development, the telencephalon undergoes remarkable changes. Artwork depicting foetal brain development showcases how this region evolves over time. Expanding beyond humans' realm alone, an electric ray provides insight into electricity and magnetism within another area called lobus electric found within cerebellum through digital illustration. Furthermore, exploring pain pathways via sensory nerves sheds light on how messages travel from injured muscles to reach our brains—highlighting yet another aspect influenced by the telencephalon. Lastly but not least important is understanding pituitary gland anatomy since it works closely with other parts of the brain including Telencephalon which controls many vital bodily functions regulated by hormones produced by Pituitary Gland Overall these images offer glimpses into both macroscopic and microscopic aspects related to Telencephalon's structure and function—a testament to its crucial role in shaping our cognition and overall well-being