Static Electricity Collection
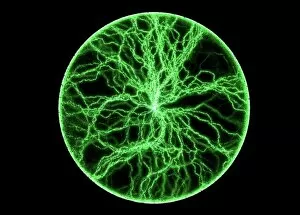
"Unleashing the Power of Static Electricity: A Journey through Centuries" Witness the mesmerizing dance of plasma within a captivating Plasma Disc
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
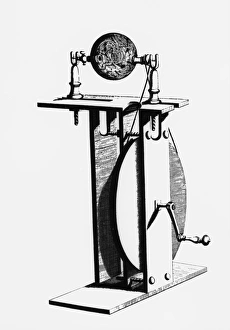
"Unleashing the Power of Static Electricity: A Journey through Centuries" Witness the mesmerizing dance of plasma within a captivating Plasma Disc, illuminating the wonders of static electricity. Step back in time to London, 1766, as Jesse Ramsden astounds with his electric machine, showcasing the early manifestations of this electrifying force. (Chromolitho) Page 49 of De Magnete by William Gilbert takes us even further back to London in 1600, where we glimpse into the historical roots and understanding of static electricity. (Print) Meet "The First Electrician" captured in a vibrant chromolitho image that showcases an individual harnessing the power for scientific exploration. Turn to page 57 of De Magnete by William Gilbert from 1600 and delve deeper into our ancestors' fascination with this mysterious phenomenon that is static electricity. (Print) Marvel at an Electroscope caught on camera, capturing a moment frozen in time when scientists sought to measure and understand electrical charges through ingenious devices. Discover how Pieter van Musschenbroek and Andreas Cunaeus revolutionized science with their discovery of the Leyden Jar in 1745 - a pivotal moment in harnessing static electricity's potential for practical use. Immerse yourself in Dutch scientists' world circa 1870 as artist CL van Kesteren brings Pieter van Musschenbroek and Andreas Cunaeus to life while they explore new frontiers within electrostatics. Explore various Electrostatic Machines from 1819 that paved the way for groundbreaking experiments and advancements in understanding this enigmatic force. Witness an awe-inspiring Electrical Experiment from 1777 depicted by artist Amedee van Loo; it encapsulates both curiosity and excitement surrounding early investigations into static electricity's behavior.