Sporangiophore Collection
Sporangiophores are fascinating structures found in various fungi, serving as the reproductive organs or fruiting bodies
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
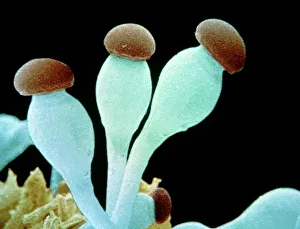
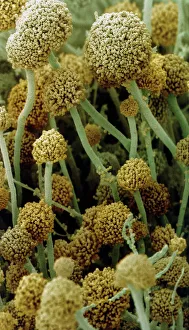
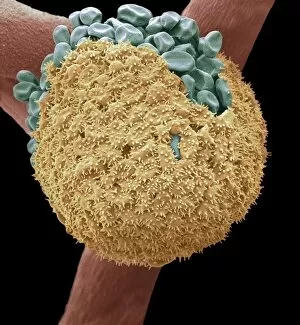
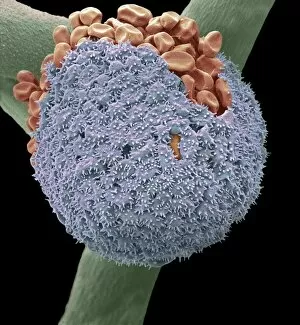
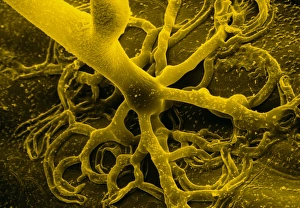
Sporangiophores are fascinating structures found in various fungi, serving as the reproductive organs or fruiting bodies. In Rhizopus oligosporus, these sporangiophores form the fruiting bodies responsible for producing spores. Similarly, Pilobolus fungus showcases its unique sporangiophores on dung, playing a crucial role in dispersal and reproduction. When examining bread mould under a scanning electron microscope (SEM), one can observe the intricate details of its sporangiophores. These hair-like threads emerge from gills of parasitized fungus like Spinellus fusiger, creating an intriguing sight. The SEM images labeled C016 / 9051, C016 / 9052, and C016 / 9050 provide us with a closer look at bread mould's sporangiophores' structure and arrangement. The delicate nature of these structures is evident through their fine thread-like appearance. Not limited to bread mould alone, fungal diseases affecting plants also exhibit sporangiophore-related symptoms. Potato blight fungus displays distinct features when observed under SEM imaging techniques. Such observations aid researchers in understanding the intricacies of potato blight infections better. Another example is downy mildew infection captured through light micrograph imagery. This image highlights how sporangiophores contribute to disease progression within plant tissues. In addition to pathogenic effects on plants, white rust fungus leaves its mark on leaves by forming visible patches caused by proliferating sporangiophores.