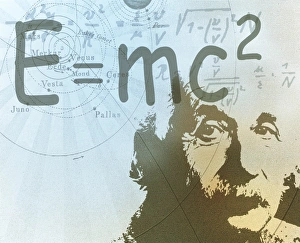Speed Of Light Collection
"Unveiling the Mysteries: Exploring the Speed of Light" In the realm of scientific wonders, few concepts have captivated our imagination like the speed of light
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
"Unveiling the Mysteries: Exploring the Speed of Light" In the realm of scientific wonders, few concepts have captivated our imagination like the speed of light. From its groundbreaking discovery by Albert Einstein to its profound implications in various fields, this fundamental cosmic constant continues to shape our understanding of the universe. Albert Einstein, a genius whose name is synonymous with revolutionary ideas, forever altered our perception of reality with his theory of relativity. Through his brilliant mind and relentless curiosity, he unraveled the secrets behind how light travels at an astonishing 299, 792 kilometers per second – a staggering velocity that defies conventional notions. The awe-inspiring phenomenon known as supernova explosion showcases nature's grandeur on an astronomical scale. In mesmerizing artwork capturing this celestial event, we witness a cataclysmic burst where immense energy propels matter into space at unimaginable speeds – reminding us just how minuscule we are in comparison. James Clerk Maxwell's contributions to electromagnetic theory earned him a place among history's greatest minds. A whimsical caricature depicts this visionary scientist who paved the way for understanding light as both waves and particles – revolutionizing physics and laying foundations for future discoveries. Another artistic portrayal brings forth Albert Einstein himself; his piercing gaze reflecting deep contemplation as he contemplates E=mc² - encapsulating mass-energy equivalence within one elegant equation. This computer artwork serves as a testament to his intellectual prowess and transformative impact on modern science. Light refraction bends rays through prisms or water droplets, revealing stunning displays such as rainbows or shimmering mirages. It reminds us that even something seemingly straightforward can hold hidden complexities waiting to be unveiled under closer scrutiny. Within particle accelerators' colossal machines lies humanity's quest for knowledge at subatomic scales. These intricate devices propel particles close to lightspeed before colliding them together – unraveling mysteries about matter's building blocks while pushing technological boundaries ever further.