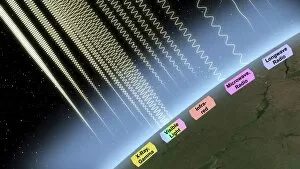
Solar Radiation Collection
"Solar Radiation: Illuminating the Wonders of the Universe" From the breathtaking Aurora (colour litho) to the magnificent Villa Tournesol
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
"Solar Radiation: Illuminating the Wonders of the Universe" From the breathtaking Aurora (colour litho) to the magnificent Villa Tournesol, it has captivated humanity for centuries. In 1814, "The Solar Spectrum" unveiled a mesmerizing display of colors emitted by our very own star. Artists like Rapine immortalized this celestial phenomenon in their artwork, depicting the ethereal curtains of Aurora Borealis or Northern Lights. Even from space, astronauts marveled at the enchanting dance of lights as they observed Aurora Borealis or Northern Lights from northern Norway on that fateful day in 1868. The captivating beauty continued to astound when Aurora Australis graced our skies in April 1994. Scientists like Alexandre Edmond Becquerel dedicated their lives to unraveling the mysteries behind solar radiation. Their groundbreaking research shed light on how energy creates organic molecules in Titan's atmosphere and paved the way for future discoveries. But solar radiation is not just about visual splendor; it holds immense power and potential. Carbon dioxide re-emitting infrared light C017 / 0787 showcases its role in Earth's climate system, reminding us of its impact on global warming. Moreover, solar radiation plays a crucial role in asteroid deflection strategies such as utilizing solar sails. These innovative technologies harness sunlight's force to propel spacecraft and potentially safeguard our planet from catastrophic collisions with asteroids. Solar radiation continues to inspire awe and fuel scientific exploration into uncharted territories. As we delve deeper into understanding its intricacies, we unlock new possibilities for sustainable energy sources and gain insights into our place within this vast universe. So let us bask in the radiance of solar phenomena while embracing its potential for innovation and discovery – a testament to humanity's relentless pursuit of knowledge amidst nature's most dazzling displays.