Sir Marc Isambard Collection
Sir Marc Isambard Brunel was a pioneering civil engineer who played a pivotal role in the construction of the Thames Tunnel in London
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
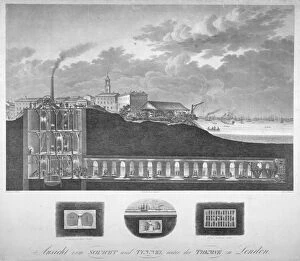
Sir Marc Isambard Brunel was a pioneering civil engineer who played a pivotal role in the construction of the Thames Tunnel in London. This remarkable feat of engineering, which began in 1825 and took 18 years to complete, revolutionized transportation and showcased Brunel's ingenuity. The proposed western archway of the Thames Tunnel, depicted in a view from around 1831, gives us a glimpse into Brunel's vision for this ambitious project, and is awe-inspiring to imagine how he transformed this underground passage beneath the River Thames into a bustling thoroughfare. In the Pathfinders painting by James Northcote from 1812, we see Sir Marc Isambard Brunel at work with his fellow engineers. Their determination and expertise laid the foundation for one of London's most iconic landmarks. The diving-bell used during construction, captured in an image from around 1878, symbolizes both danger and innovation. This device allowed workers to descend into great depths while ensuring their safety—a testament to Brunel's commitment to protecting his workforce. When it finally opened for traffic in its original form around 1872, the Thames Tunnel became an instant marvel. Its interior view from 1830 reveals an impressive structure that seamlessly merged functionality with architectural elegance. Jules Louis Arnout's artwork from 1854 showcases the entrance to this subterranean wonderland—an invitation for visitors to explore its hidden depths and experience firsthand what had once seemed impossible. The shield used during construction (depicted by an artist in 1835) demonstrates how Brunel overcame immense challenges such as water pressure and unstable soil conditions. His innovative tunneling methods set new standards for future projects worldwide. Detailed plans, sections, and elevations created by E Turrell in 1835 provide insight into the meticulous planning behind every aspect of this grand undertaking, and is through these documents that we can truly appreciate Brunel's genius.