Seismology Collection
Seismology: Unveiling the Secrets of Earth's Tremors From the depths of our planet to the vastness of space
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
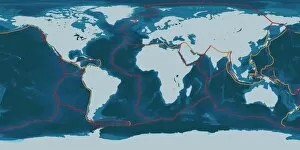
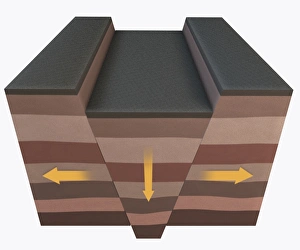
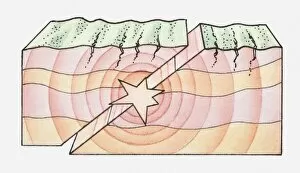
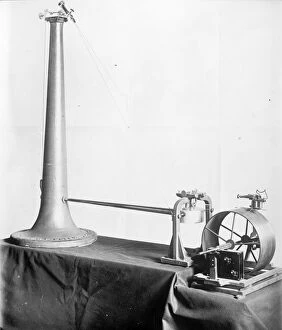
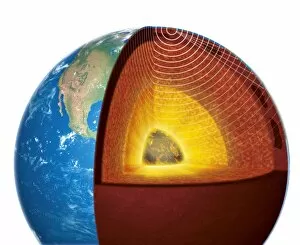
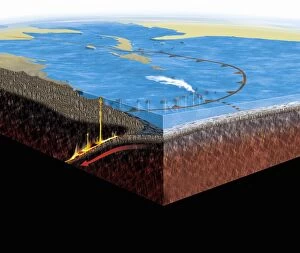
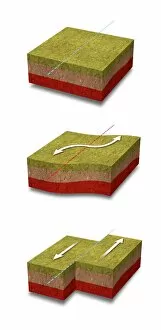
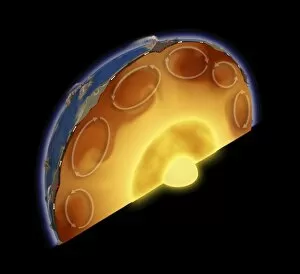
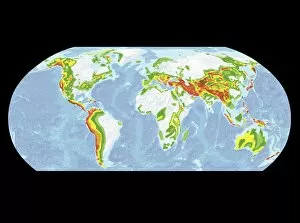
Seismology: Unveiling the Secrets of Earth's Tremors From the depths of our planet to the vastness of space, it has been instrumental in unraveling the mysteries that lie beneath our feet. By studying seismic waves and their effects, scientists have gained invaluable insights into Earth's tectonic plates and the forces that shape our world. A breathtaking aerial view captures the infamous San Andreas fault snaking through California, a visible reminder of the immense power locked within these shifting plates. It serves as a constant reminder of nature's unpredictability and humbles us with its potential for destruction. In July 1969, Buzz Aldrin meticulously sets up a seismic experiment during Apollo II mission under Neil Armstrong's watchful eye. This groundbreaking moment marked humanity's first attempt to understand moonquakes and paved the way for future lunar explorations. The contributions made by Luigi Palmieri, an Italian geophysicist in 1893, cannot be overstated. His pioneering work on seismographs revolutionized earthquake detection and monitoring systems worldwide. Today we can marvel at one such seismograph proudly displayed at Selfridges on Oxford Street in London – a testament to human ingenuity. An awe-inspiring illustration vividly depicts an earthquake in all its terrifying grandeur - buildings crumbling, ground splitting apart - reminding us of both its destructive force and scientific significance. Such events are captured by seismologists who tirelessly analyze data from around the globe to better comprehend these natural phenomena. A diagram showcasing different types of tectonic plate boundaries further deepens our understanding. From convergent boundaries where plates collide fiercely to divergent boundaries where new crust is born amidst volcanic activity – each interaction shapes landscapes over millions of years. Transporting us back in time, an artwork depicting Early Earth globe offers a glimpse into our planet's ancient past when continents were still forming and life was taking its first steps towards complexity. Seismology allows us to piece together this intricate puzzle of Earth's history.