Sarcomere Collection
The sarcomere, the fundamental unit of muscle contraction, is a microscopic marvel found in various types of muscles throughout the body
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
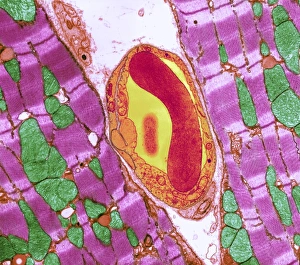
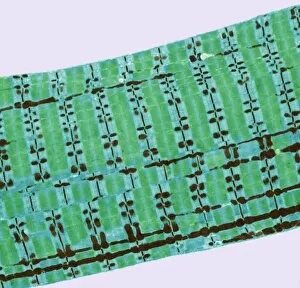
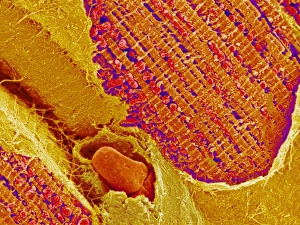
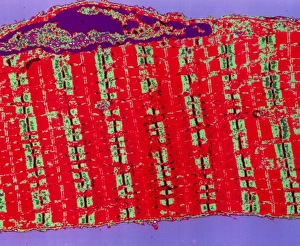
The sarcomere, the fundamental unit of muscle contraction, is a microscopic marvel found in various types of muscles throughout the body. In the heart muscle, this intricate structure can be visualized under a confocal light micrograph or through transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The TEM images reveal the highly organized arrangement of sarcomeres within cardiac muscle fibers and their close association with capillaries that supply vital nutrients. Understanding sugar uptake in muscles becomes clearer when examining diagrams illustrating this process. These illustrations demonstrate how glucose is transported into skeletal muscles to provide energy for movement. TEM images further showcase the detailed organization of sarcomeres within skeletal muscle fibers, highlighting their role in generating force and facilitating voluntary movements. Not limited to skeletal muscles alone, cardiac muscle also exhibits an abundance of sarcomeres as seen through TEM and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) techniques. These high-resolution images capture the unique structural features present in cardiac tissue, emphasizing its ability to contract rhythmically and pump blood efficiently. Intriguingly, human muscle fibers exhibit distinct characteristics when depicted diagrammatically. These diagrams help us comprehend the diversity among different types of muscle fibers based on factors such as size, composition, and function.