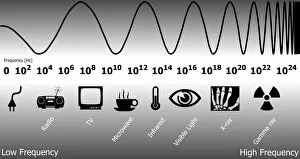
Radiation Collection (page 3)
"Unveiling the Mysteries of Radiation: From Cosmic Background to Nuclear Fallout" In our quest to understand the universe
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
"Unveiling the Mysteries of Radiation: From Cosmic Background to Nuclear Fallout" In our quest to understand the universe, it has emerged as a fascinating and enigmatic force. Embark on a captivating journey through time and space as we explore the various facets of this phenomenon. Let's begin with the MAP microwave background, an extraordinary snapshot of our early universe. This relic radiation allows us to peer back in time, unraveling secrets about the birth and evolution of galaxies. Gaze upon the mesmerizing Orion Nebula, where cosmic microwave background radiation intertwines with celestial beauty. The swirling gases and dazzling stars within M42 and M43 create a breathtaking spectacle that showcases both creation and destruction. Venturing further into history, we encounter James Clerk Maxwell, depicted in caricature form. His groundbreaking work paved the way for understanding electromagnetic waves - including radiation - forever changing our perception of physics. As we traverse through time on our Universe timeline artwork, witness a supernova explosion frozen in motion. This awe-inspiring display captures nature's power at its peak while shedding light on how radiation shapes celestial bodies throughout their lifecycle. But not all forms are born from distant realms; some have been man-made. Recall the haunting aftermath of a 1957 nuclear test: Fall-out lingers ominously over landscapes like ghost villages in Belarus – stark reminders of humanity's complex relationship with atomic energy. Marvel at the ethereal Helix Nebula, adorned by planetary nebulae emitting radiant hues. These intricate formations showcase how dying stars release their outer layers into space – an exquisite dance between life cycles and cosmic emissions. Finally, confront one of nature's most enigmatic creations: black holes. These gravitational powerhouses emit intense streams of high-energy particles known as Hawking Radiation – offering tantalizing clues about what lies beyond event horizons. Radiation remains an enigma that captivates scientists and artists alike; it is both a cosmic fingerprint and an earthly creation.