Protein Spike Collection
"Unveiling the Intricate Protein Spike: A Closer Look at HIV Particles" Intriguing and enigmatic
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
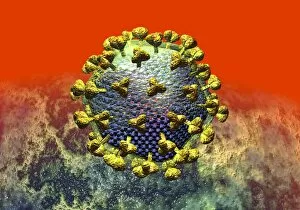
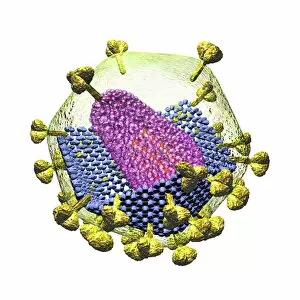
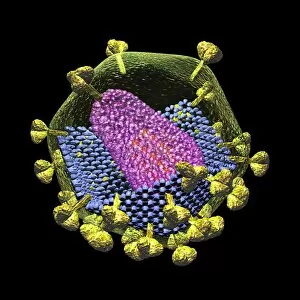
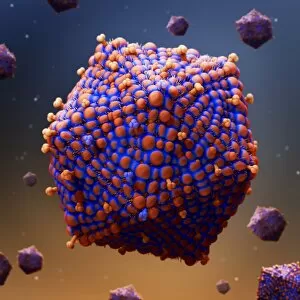
"Unveiling the Intricate Protein Spike: A Closer Look at HIV Particles" Intriguing and enigmatic, the protein spike found on HIV particles has long fascinated scientists and artists alike. Captured in stunning artwork such as C016 / 9141, C016 / 9142, C016 / 8659, and more, these images offer a glimpse into the complex structure of this viral component. At first glance, these captivating illustrations showcase the unique shape of the protein spike protruding from the surface of HIV particles. Its distinctive appearance resembles a crown or corona - hence its name "spike. " However, beneath its aesthetic allure lies a crucial role in HIV's ability to infect human cells. Functioning as a key for cellular entry, this protein spike serves as an essential tool for HIV's survival. It binds with specific receptors on target cells like a lock fitting into its corresponding keyhole. This interaction initiates a cascade of events that ultimately allows the virus to invade and hijack healthy cells within our immune system. The intricate details captured in artworks like C016 / 8658, C016 / 8655, and others highlight how each individual component contributes to this process. The precise arrangement of amino acids forming helices and loops creates an elaborate network that enables efficient attachment to host cell receptors. Moreover, exploring images such as those depicted in C016 / 8654 or C016 / 8652 reveals variations among different strains of HIV particles. These subtle differences can impact their ability to bind effectively with certain receptors or evade immune responses – factors critical for understanding disease progression and developing potential treatments. As we delve deeper into these mesmerizing depictions like those seen in artwork C016/8649 or C016/8651, C106/8650, we gain valuable insights into both scientific research and artistic interpretation.