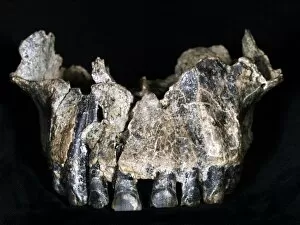
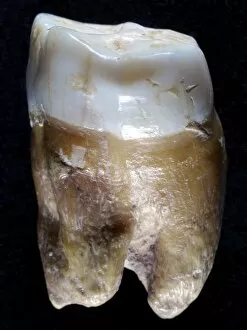
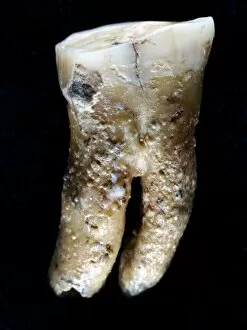
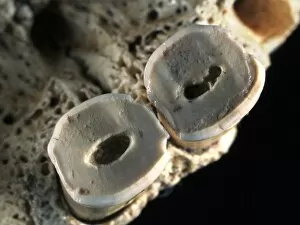
Paleolithic Collection (page 8)
"Journey into the Paleolithic: Exploring Stone-Age Cave Paintings and Ancient Artifacts" Step back in time as we delve into the fascinating world of the Paleolithic era
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
"Journey into the Paleolithic: Exploring Stone-Age Cave Paintings and Ancient Artifacts" Step back in time as we delve into the fascinating world of the Paleolithic era. From the breathtaking replica of Lascaux II cave paintings to the mesmerizing stone-age cave paintings found in Chauvet, France, these ancient artworks offer a glimpse into our distant past. In Chauvet, France, we are transported to a time when early humans expressed their creativity through intricate drawings on cave walls. The detailed depictions of animals and scenes from everyday life provide valuable insights into their culture and way of living. As we venture further, we encounter more captivating finds such as the Venus of Brassempouy - a small ivory figurine representing one of humanity's earliest known representations of a human face. This delicate artifact reminds us that art has always been an essential part of our existence. Moving across borders, Spain reveals its own treasure trove at Altamira Caves in Santillana de Mar. Here, bison come alive with remarkable realism on rock surfaces. These masterpieces showcase not only artistic talent but also an intimate connection between early humans and nature. Back in France, Pech Merle cave presents us with another extraordinary sight - dotted patterns adorning its walls like celestial constellations. These enigmatic markings leave us pondering their significance and purpose within this ancient society. The journey wouldn't be complete without mentioning the iconic Venus figures that have captivated archaeologists for centuries. From Venus of Laussel to various other iterations found throughout Europe during this period, these sculptures symbolize fertility and female power while shedding light on gender roles prevalent at that time. Finally, let's not forget about one of the most famous pieces from Lascaux - Bison from Nave. Standing tall at 7 feet and 5 inches high, this majestic creature showcases Style III artwork dating back to approximately 15, 000 B. C.