Neutrophil Collection
Neutrophils: The Mighty Warriors of our Immune System Neutrophils, the unsung heroes of our immune system
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
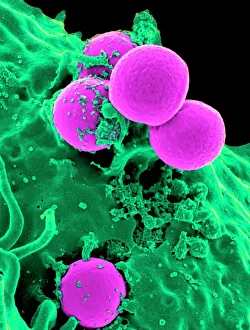
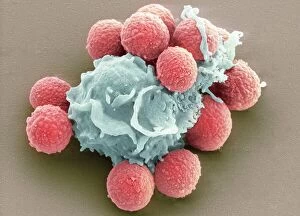
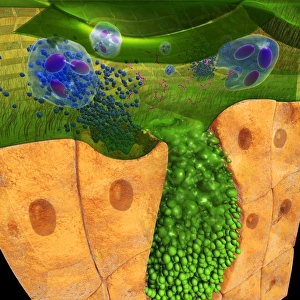
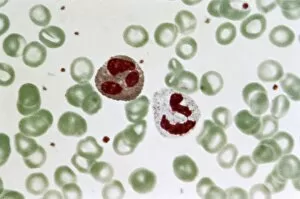
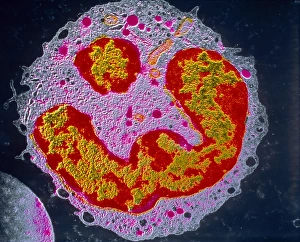
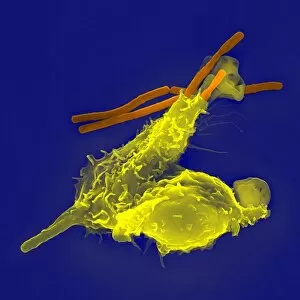
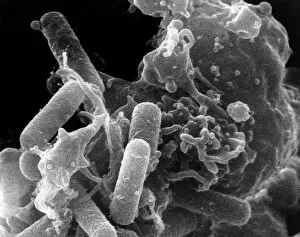
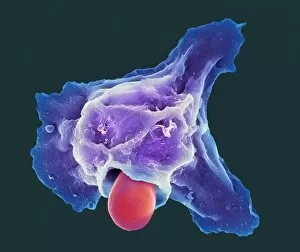
Neutrophils: The Mighty Warriors of our Immune System Neutrophils, the unsung heroes of our immune system, play a crucial role in defending our bodies against harmful invaders. These microscopic warriors are constantly on the lookout for any signs of trouble. In one remarkable image (SEM C018 / 8596), we witness the sheer power of neutrophils as they engulf MRSA, a notorious antibiotic-resistant bacterium. This process, known as phagocytosis, is their primary weapon against such threats. Another intriguing micrograph reveals Dohle bodies within these blood cells. These structures (micrograph) serve as indicators of infection or inflammation and help us understand the state of our immune response. But it doesn't stop there. Neutrophils also take on fungal spores with equal determination. In an astonishing SEM image capturing this battle (Phagocytosis of fungal spores), we witness their relentless pursuit to keep us safe from harm. A digital cross-section illustration provides insight into how neutrophils combat rhinovirus in our nasal cavity by producing antibodies. This intricate defense mechanism showcases their versatility and adaptability in fighting off various pathogens. Examining a blood smear under a light microscope (F005 / 6090) allows us to appreciate the abundance and diversity of these valiant defenders circulating within us. Their presence signifies an active immune response at work. Sometimes even neutrophils fall victim to their battles; another SEM image shows them alongside MRSA casualties (SEM C018 / 8601). It serves as a reminder that while they may be powerful, they too face risks when protecting us from harm's way. Acute bronchitis can cause distressing symptoms but fear not – neutrophils come to the rescue once again. A light micrograph captures these brave soldiers combating bronchial inflammation (F006 / 9803).