Neurone Collection (page 4)
Neurons, the fundamental building blocks of our nervous system, are intricate and fascinating cells that enable communication within our bodies
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
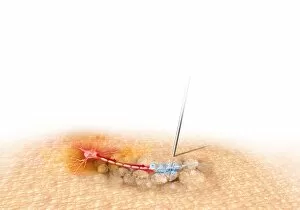
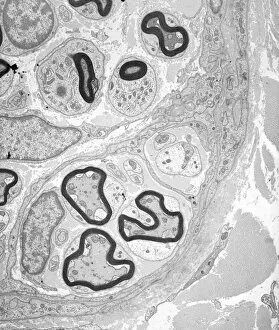
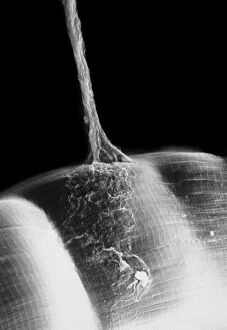
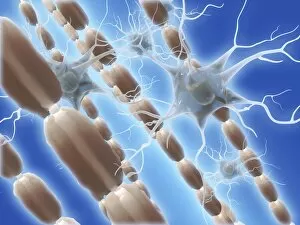
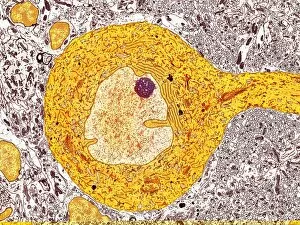
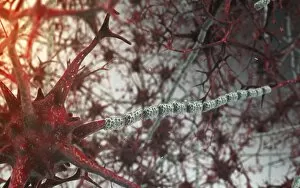
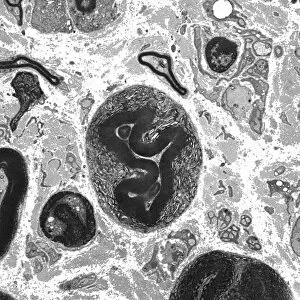
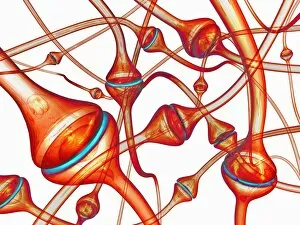
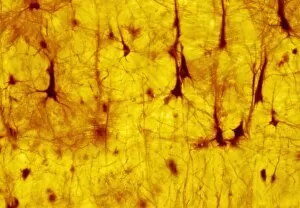
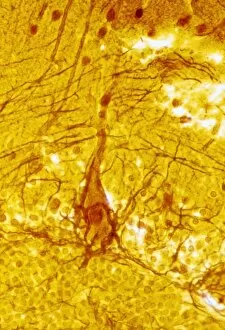
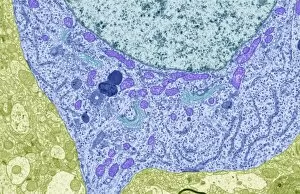
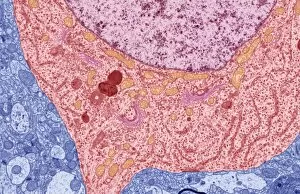
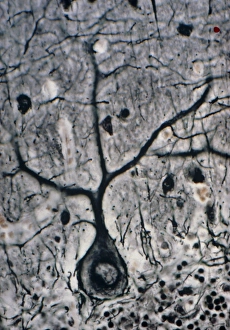
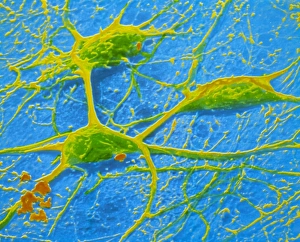
Neurons, the fundamental building blocks of our nervous system, are intricate and fascinating cells that enable communication within our bodies. This captivating image showcases nerve and glial cells under a light microscope, revealing their unique structures and functions. In another stunning capture, we witness the synapse nerve junction through a transmission electron microscope (TEM), where signals are transmitted between neurons. The complexity of this microscopic world is further highlighted in an immunofluorescent light micrograph depicting neurons and astrocytes, emphasizing their role in supporting neuronal function. A striking scanning electron microscope (SEM) image zooms in on a single nerve cell, showcasing its intricate details and delicate branching structure. These specialized cells play a crucial role in transmitting electrical impulses throughout our body's complex network. Moving beyond individual cells, we explore the vastness of glial stem cell culture under a light microscope. These versatile cells have the potential to differentiate into various types of support cells for neurons. The importance of blood supply to brain tissue is beautifully illustrated in an image capturing the cerebral cortex's intricate network of nerve cells nourished by tiny blood vessels. This symbiotic relationship ensures optimal functioning of our cognitive abilities. Delving deeper into neural stem cell culture reveals their remarkable ability to self-renew and differentiate into different types of brain cells. These incredible properties hold immense promise for regenerative medicine and understanding neurological disorders better. Lastly, we observe motor neurons under a light microscope—key players responsible for transmitting signals from the central nervous system to muscles or glands throughout our body. Their precise organization allows us to perform coordinated movements effortlessly. These captivating images provide glimpses into the mesmerizing world of neurones—a testament to nature's intricacy and beauty as they orchestrate every thought, sensation, movement within us while unraveling mysteries that continue to captivate scientists worldwide.