Myosin Collection
Myosin: The Mighty Molecular Motor of Muscle Contraction In the intricate world of muscle biology
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
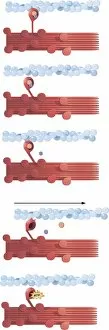
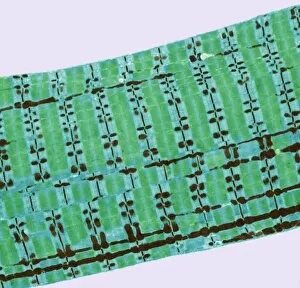
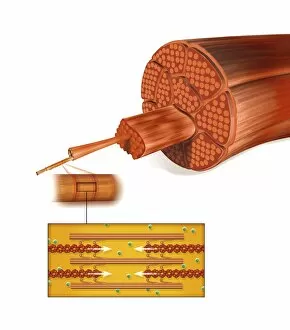
Myosin: The Mighty Molecular Motor of Muscle Contraction In the intricate world of muscle biology, myosin takes center stage as a vital player in the fascinating process of muscle contraction. This confocal light micrograph showcases the awe-inspiring beauty within heart muscle, highlighting its crucial role in sustaining life. Delving deeper into muscle fiber structure, an artwork captures the complexity and elegance of this microscopic marvel. Myosin molecules intricately interlock with actin filaments to generate force and enable movement, creating a symphony of motion within our bodies. Illustrations vividly depict how myosin powers muscle contraction. With labels guiding us through each step, we witness the coordinated dance between these molecular motor proteins and actin filaments that results in muscular movement - from flexing our biceps to pumping blood through our veins. However, sometimes even mighty they can face challenges. A close-up reveals details of deep back muscles experiencing sprain, strain, or spasm – reminders that proper care is essential for maintaining their health and functionality. Zooming further into the microscopic realm unveils torn muscle fibers surrounded by healing stages. It serves as a testament to both the resilience and regenerative capacity possessed by our body's remarkable machinery. Examining individual components brings us face-to-face with myosin itself – F006/9618 molecule stands tall as a molecular motor protein responsible for powering countless contractions throughout our lifetime. Its counterparts include Myosin molecule F006/9255 and Myosin fragment molecule F006/9245 - all working tirelessly behind-the-scenes to keep us moving effortlessly. An artistic representation called Actin Myosin Muscle Model (artwork C014/2661) offers insight into how these proteins interact on a larger scale. Their harmonious collaboration ensures smooth functioning across various muscles in our body while enabling strength and agility.