Monocyte Collection
Monocyte: The Versatile Warrior of the Immune System Dendritic cells, artwork, and activated macrophages, SEM C015 / 6375
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
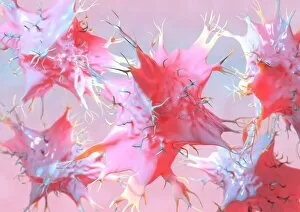
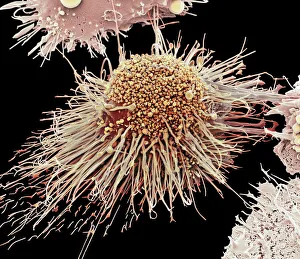
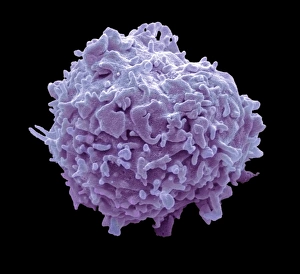
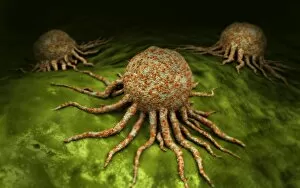
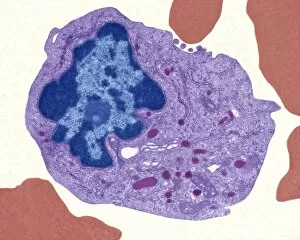
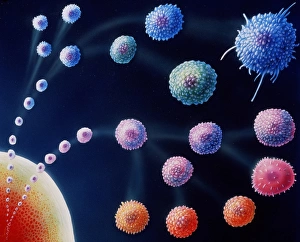
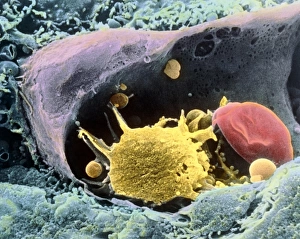
Monocyte: The Versatile Warrior of the Immune System Dendritic cells, artwork, and activated macrophages, SEM C015 / 6375, join forces with monocytes to form a formidable defense against pathogens, and are white blood cells that play a crucial role in our immune system's response. In this captivating artwork depicting dendritic cells, we witness their intricate structure and ability to capture antigens for presentation to other immune cells. These powerful warriors act as messengers between the innate and adaptive immune systems. Activated macrophages, SEM C016 / 3089, showcase their unique morphology after encountering foreign invaders. They engulf these intruders through phagocytosis while releasing inflammatory mediators to recruit more immune cells into action. Conceptual images of cancer viruses remind us of monocytes' significance in combating malignant growths. These resilient soldiers infiltrate tumors and initiate an anti-cancer response by presenting tumor-specific antigens to T-cells. Microscopic views reveal phagocytic macrophages at work—devouring harmful particles with precision and efficiency. Their collective strength is evident as they form a group ready to defend our bodies from any threat that may arise. A mesmerizing 3D rendering showcases macrophage phagocytosis—a process where these vigilant guardians engulf bacteria or debris within their cytoplasmic extensions called pseudopods. This remarkable mechanism ensures the removal of potential dangers from our system. Amidst the microscopic view of phagocytic macrophages lies another glimpse of cancer virus particles—an ongoing battle between health and disease unfolds before our eyes. Monocytes stand firm in this struggle against malignancy alongside other components of our immune arsenal. Monocytes prove themselves indispensable in safeguarding our well-being by actively participating in various immunological processes. From capturing antigens to devouring pathogens or even fighting cancerous threats head-on—they epitomize the resilience and adaptability of our immune system.