Microorganism Collection (page 5)
Microorganisms, the tiny life forms that exist all around us, are truly fascinating
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
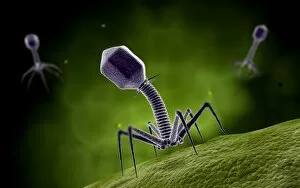
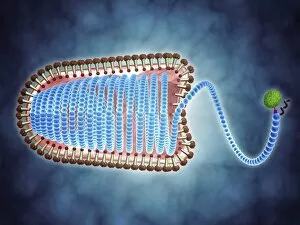
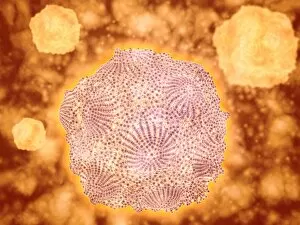
Microorganisms, the tiny life forms that exist all around us, are truly fascinating. From HeLa cells to water bears and viruses like MRSA and RSV, these microscopic entities play a significant role in our lives. In the world of science, HeLa cells have been instrumental in numerous breakthroughs. Captured under a light micrograph (C017 / 8299), their intricate structures reveal the complexity of human biology. Another captivating image shows neutrophils engulfing MRSA bacteria, as seen through a scanning electron microscope (C018 / 8596). This powerful defense mechanism showcases how our immune system fights against harmful invaders. Water bears, also known as tardigrades, are remarkable creatures that can survive extreme conditions. A light micrograph (C016 / 8581) captures their unique appearance with their stout bodies and claw-like limbs. Equally intriguing is another image taken using a scanning electron microscope (SEM C016 / 9084), which reveals even more details about these resilient organisms. Viruses such as respiratory syncytial virus and flu virus particles have caused widespread infections throughout history. While one can only be observed under a microscope (microscopic view of human respiratory syncytial virus), the other is depicted through artwork showcasing its structure (flu virus particle, artwork F008 / 3245). These images remind us of the importance of vaccinations in preventing viral outbreaks. The spread of infections by sneezing is illustrated through an artistic representation (artwork C013 / 5949). It serves as a reminder to practice good hygiene to protect ourselves and others from contagious diseases. Chlamydia may be small but has significant consequences for those affected by it. A microscopic view highlights its presence within host cells—a stark reminder of the need for awareness and prevention efforts against sexually transmitted infections. Looking back at historical lithographs from 1906 brings attention to colonies formed by Haemophilus influenzae and Mycobacterium leprae.